- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
-
Neck muscles
- Superficial neck muscles
- Scalene muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Prevertebral muscles
- Suboccipital muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Sternothyroid
The sternothyroid (Latin: musculus sternothyroideus) is a thin strap-like neck muscle belonging to the infrahyoid muscles together with the omohyoid, sternohyoid and thyrohyoid. It extends between the sternum and thyroid cartilage of the larynx. The sternothyroid is also classified as one of the anterior neck muscles.
| Sternothyroid | |
| Origin | Manubrium of sternum |
| Insertion | Thyroid cartilage |
| Action | Depresses larynx |
| Innervation | Anterior rami of 1st to 3rd cervical spinal nerves (C1-C3) via ansa cervicalis |
| Blood supply | Superior thyroid and lingual arteries |
Origin
The sternothyroid originates from the manubrium of the sternum.
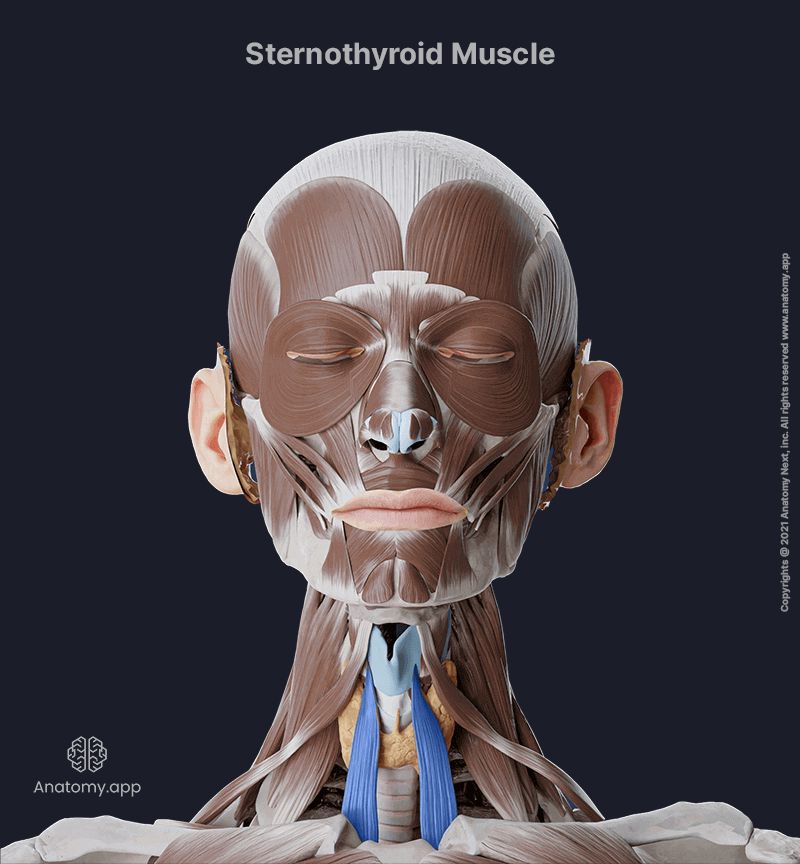
Insertion
The sternothyroid muscle inserts on the oblique line of the thyroid cartilage.
Action
Upon contraction, the sternothyroid depresses the larynx.
Innervation
The sternothyroid muscle is innervated by the anterior rami of the 1st to 3rd cervical spinal nerves (C1 - C3) via the ansa cervicalis of the cervical plexus.
Blood supply
The sternothyroid muscle receives arterial blood supply from the superior thyroid and lingual arteries. Both are branches of the external carotid artery.