- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
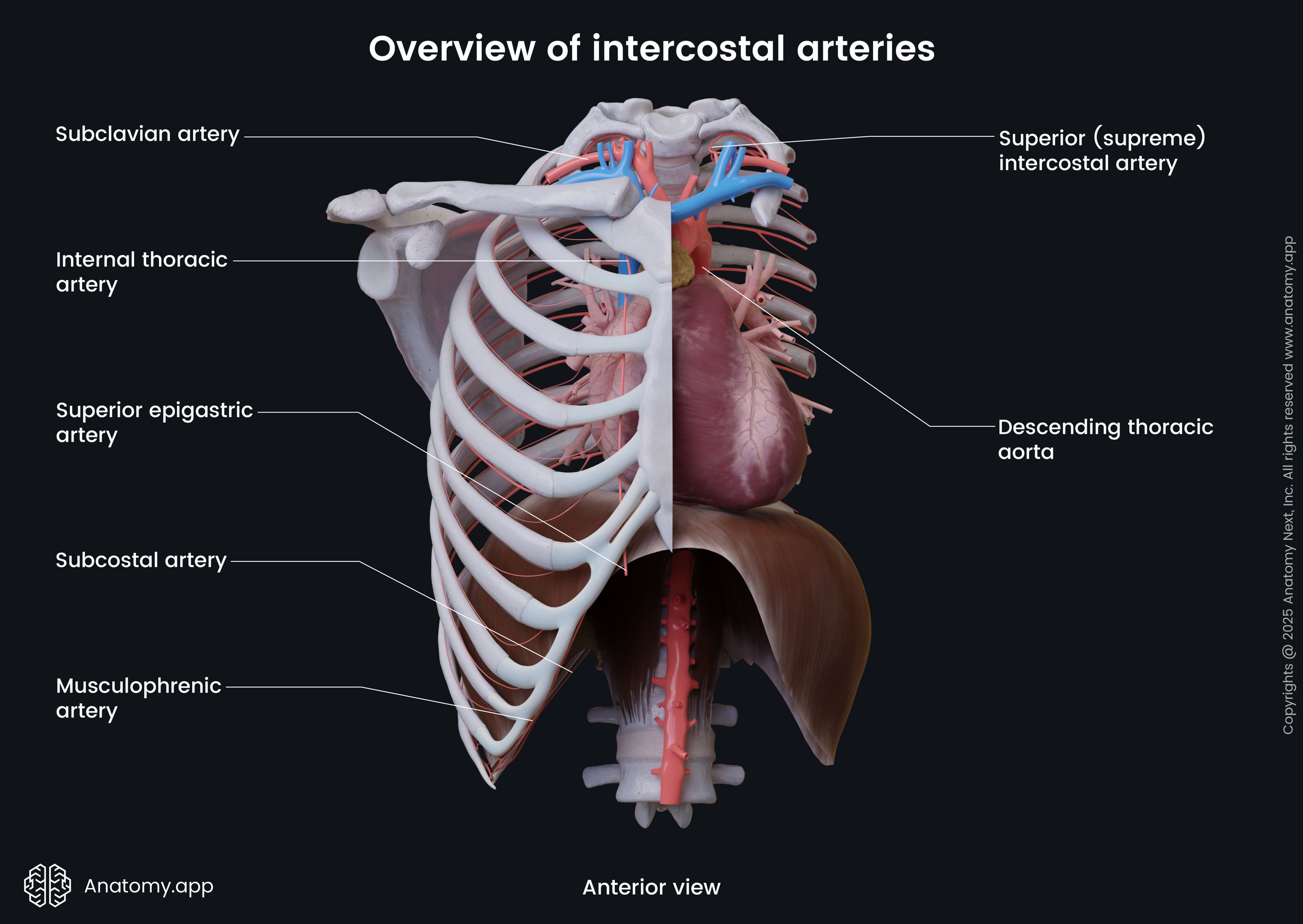
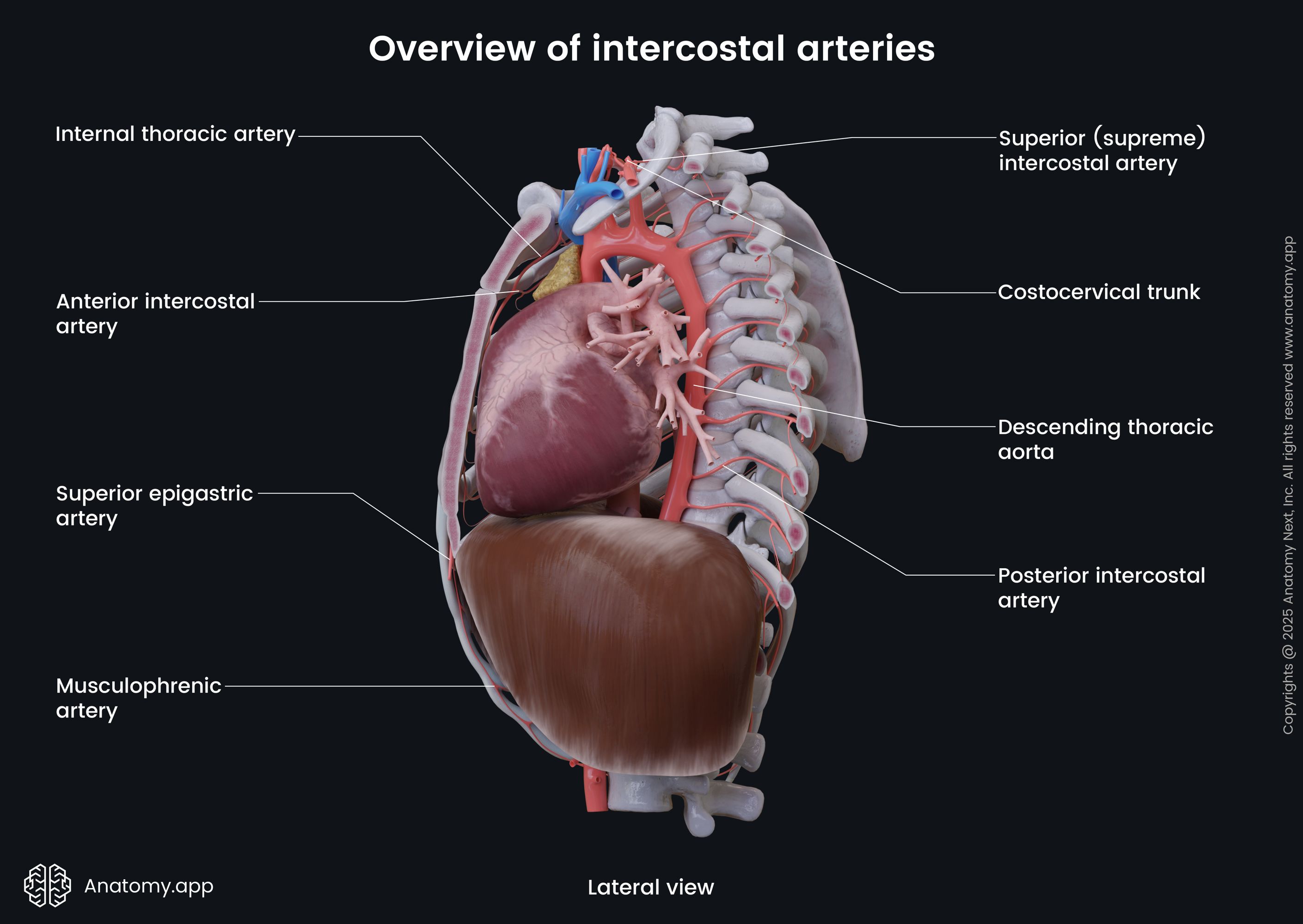
Posterior intercostal arteries
The posterior intercostal arteries are eleven pairs of blood vessels that travel within the intercostal spaces and supply the thoracic wall and parietal pleura. The upper two branch off the superior intercostal artery, while the lower nine pairs arise directly from the thoracic aorta. Together with the anterior intercostal arteries, the posterior intercostal arteries supply the muscles and other components of the intercostal spaces and the parietal pleura. The posterior intercostal arteries also give branches to the skin, muscles and other structures in the back.
Course of posterior intercostal arteries
The posterior intercostal arteries arise from the back of the thoracic aorta. On the right side, these arteries are longer because the aorta lies to the left of the midline. They travel in front of the vertebrae and behind vessels of the azygos venous system, esophagus, and thoracic duct. On the left side, the posterior intercostal arteries pass posteriorly adjacent to the vertebrae and enter the intercostal spaces.
The posterior intercostal arteries that arise directly from the aorta supply the lower nine intercostal spaces. The upper two spaces are supplied by branches of the superior intercostal artery (and these branches are sometimes also referred to as posterior intercostal arteries). The superior intercostal artery is a branch of the costocervical trunk, which arises from the subclavian artery.
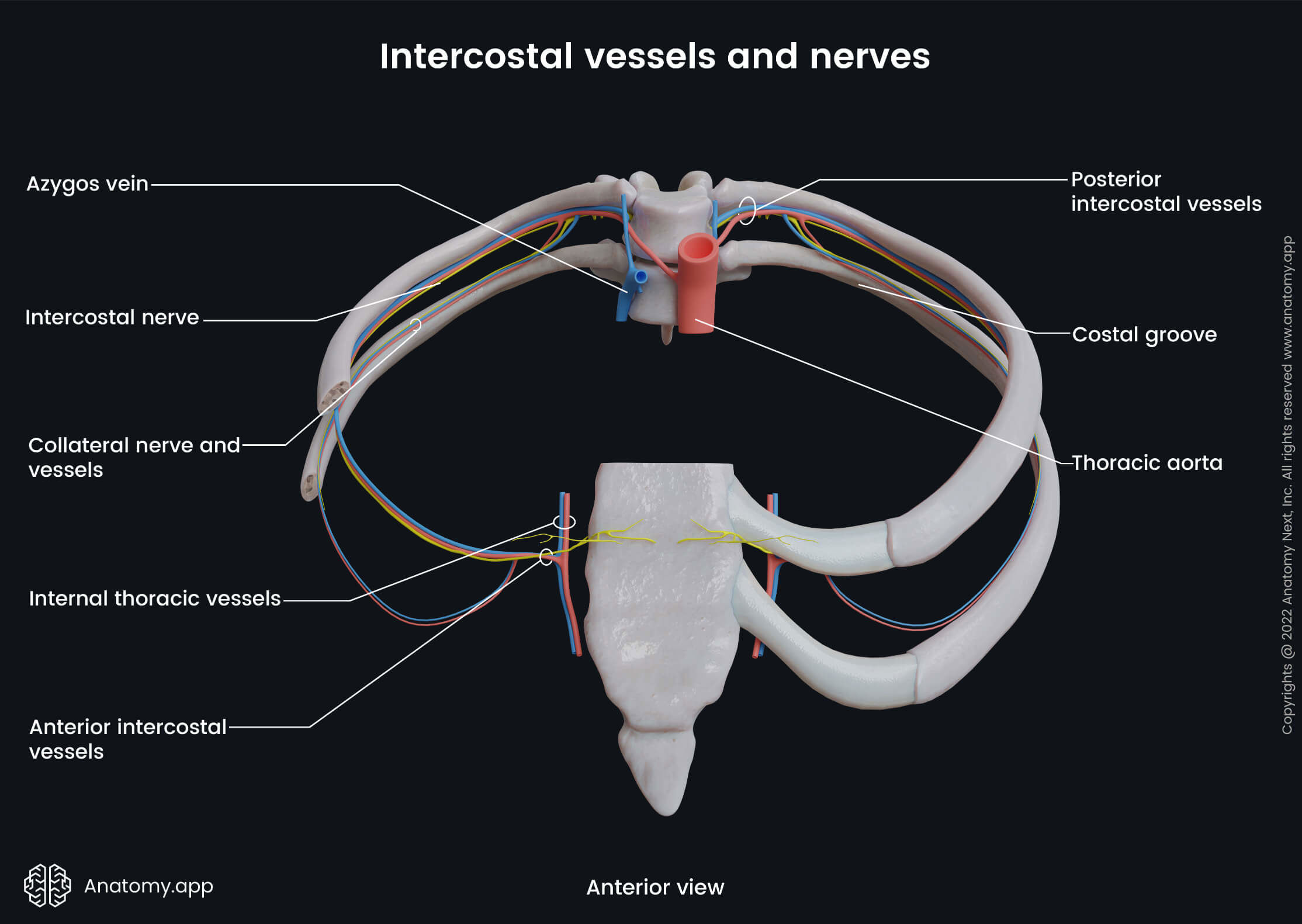
Branches of posterior intercostal arteries
Each posterior intercostal artery divides into two branches anterior and posterior. The anterior branch passes along the costal groove (found on the internal surface of a rib). Within the groove, the anterior branch of the posterior intercostal artery is accompanied by an intercostal vein and nerve. The anterior branch further splits into four branches:
- Collateral intercostal branch
- Lateral cutaneous branch
- Mammary branch
- Muscular branch
The posterior branch of the posterior intercostal artery gives rise to branches that anastomose with other vessels to supply the spinal cord, as well as soft tissue structures of the back.