- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Perineal nerve
The perineal nerve (Latin: nervus perinealis) is the larger terminal branch of the pudendal nerve that innervates the perineal region. It is a mixed nerve containing motor and sensory fibers.
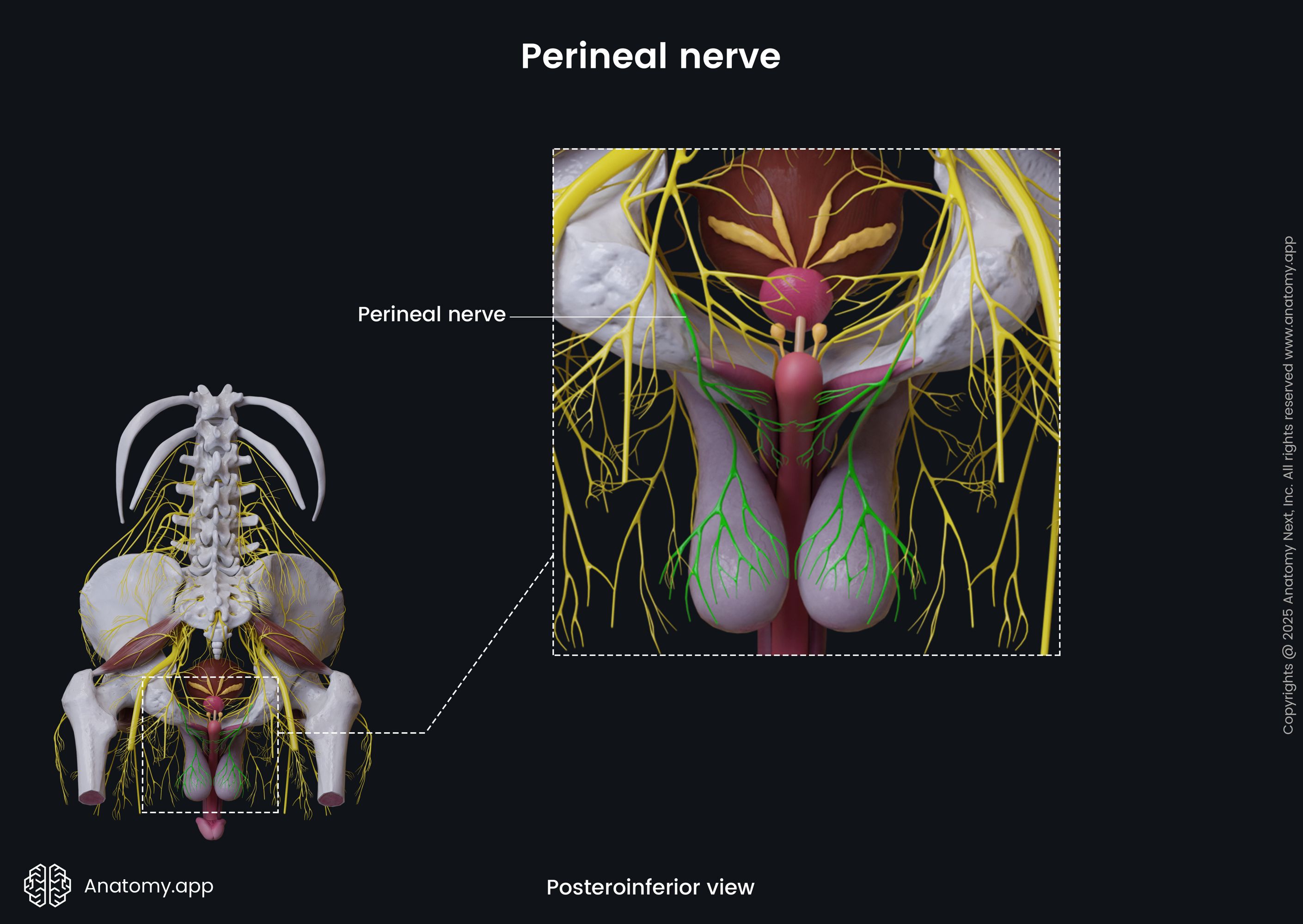
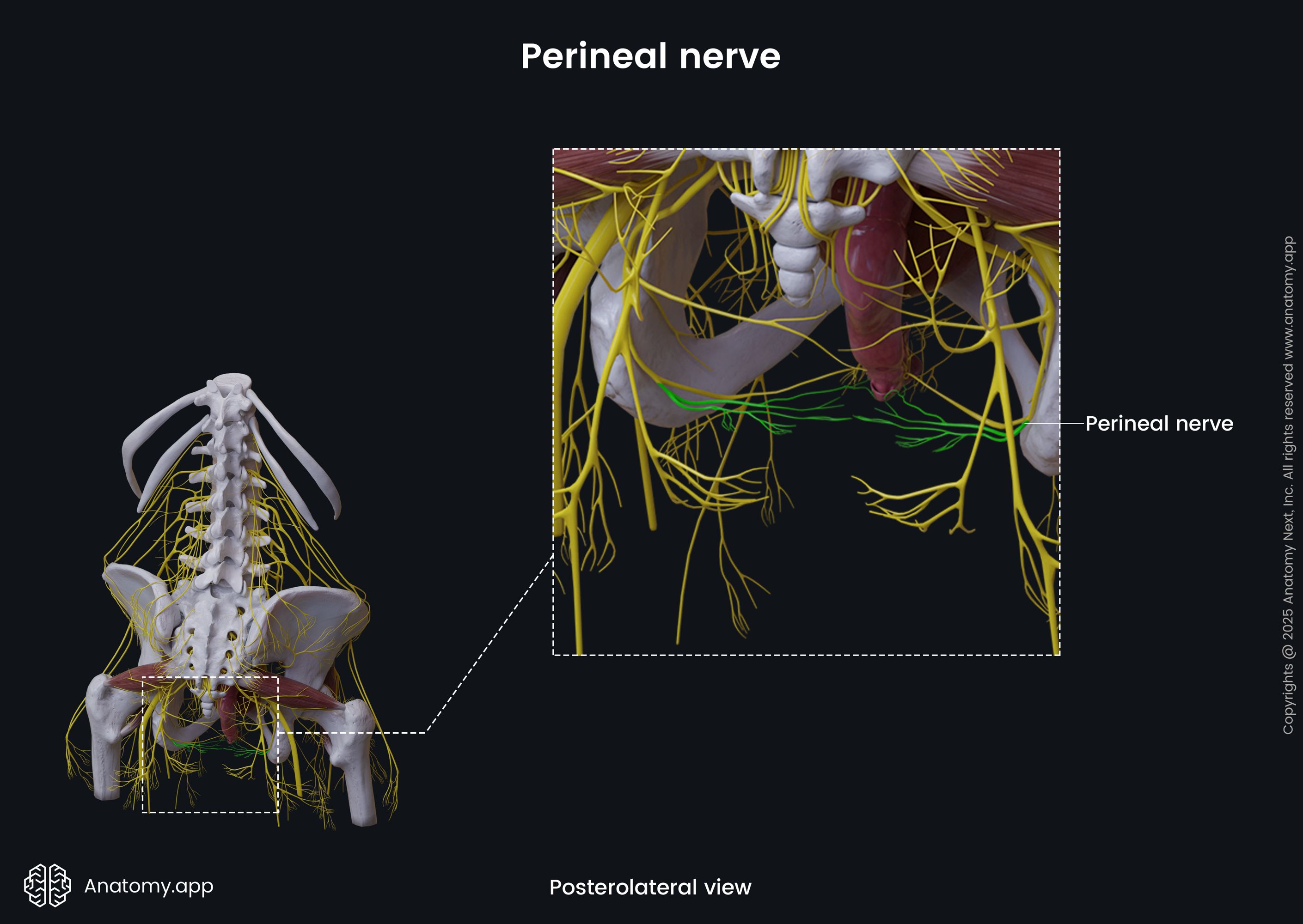
The perineal nerve runs ventrally in the urogenital triangle, accompanies the perineal artery and divides into the posterior scrotal (or labial) and muscular branches.
The posterior scrotal (for males) or posterior labial nerve (for females) gives off medial and lateral branches that innervate the skin of the scrotum in a male, while in a female innervating labia majora and the lower part of the vagina.
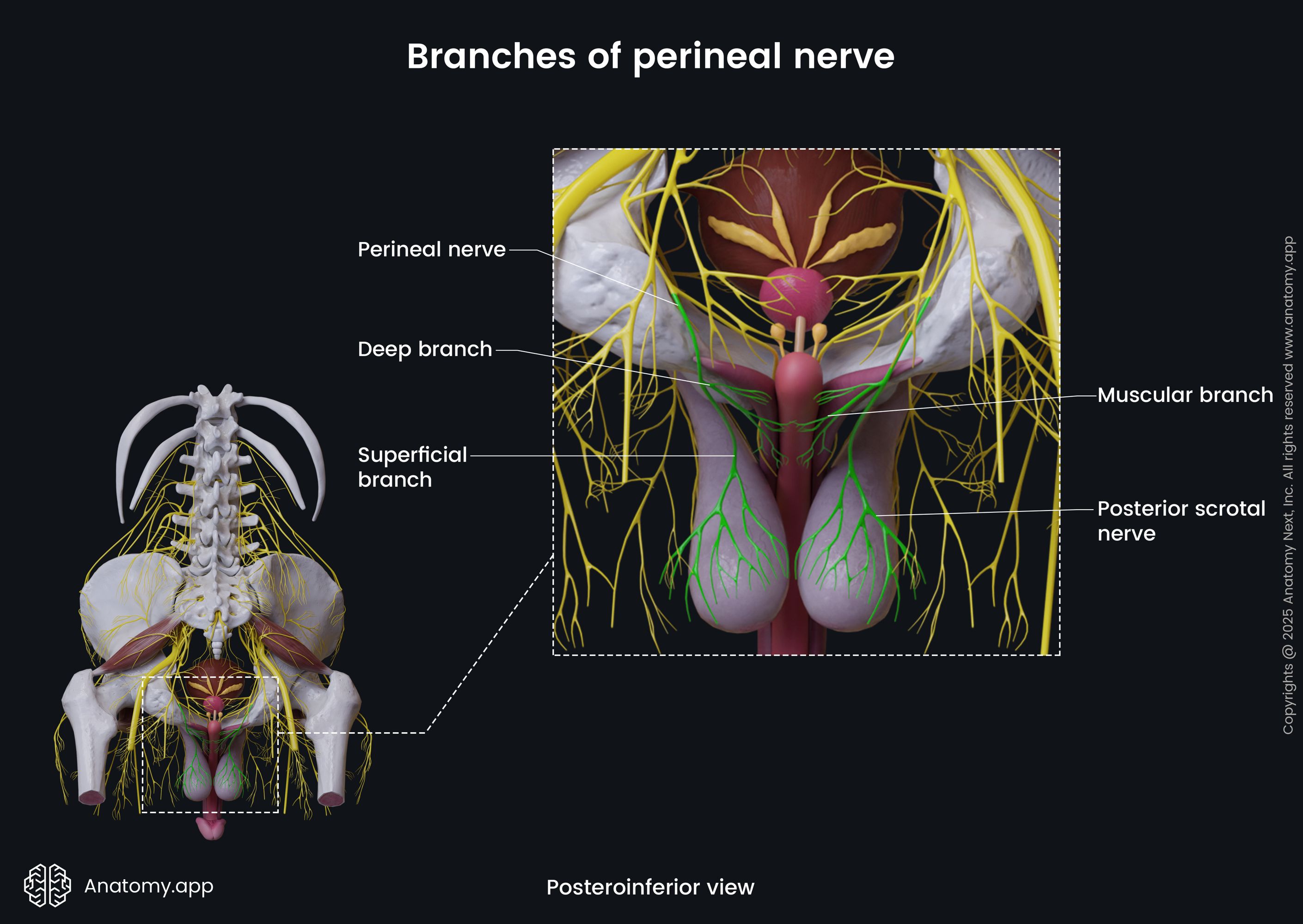
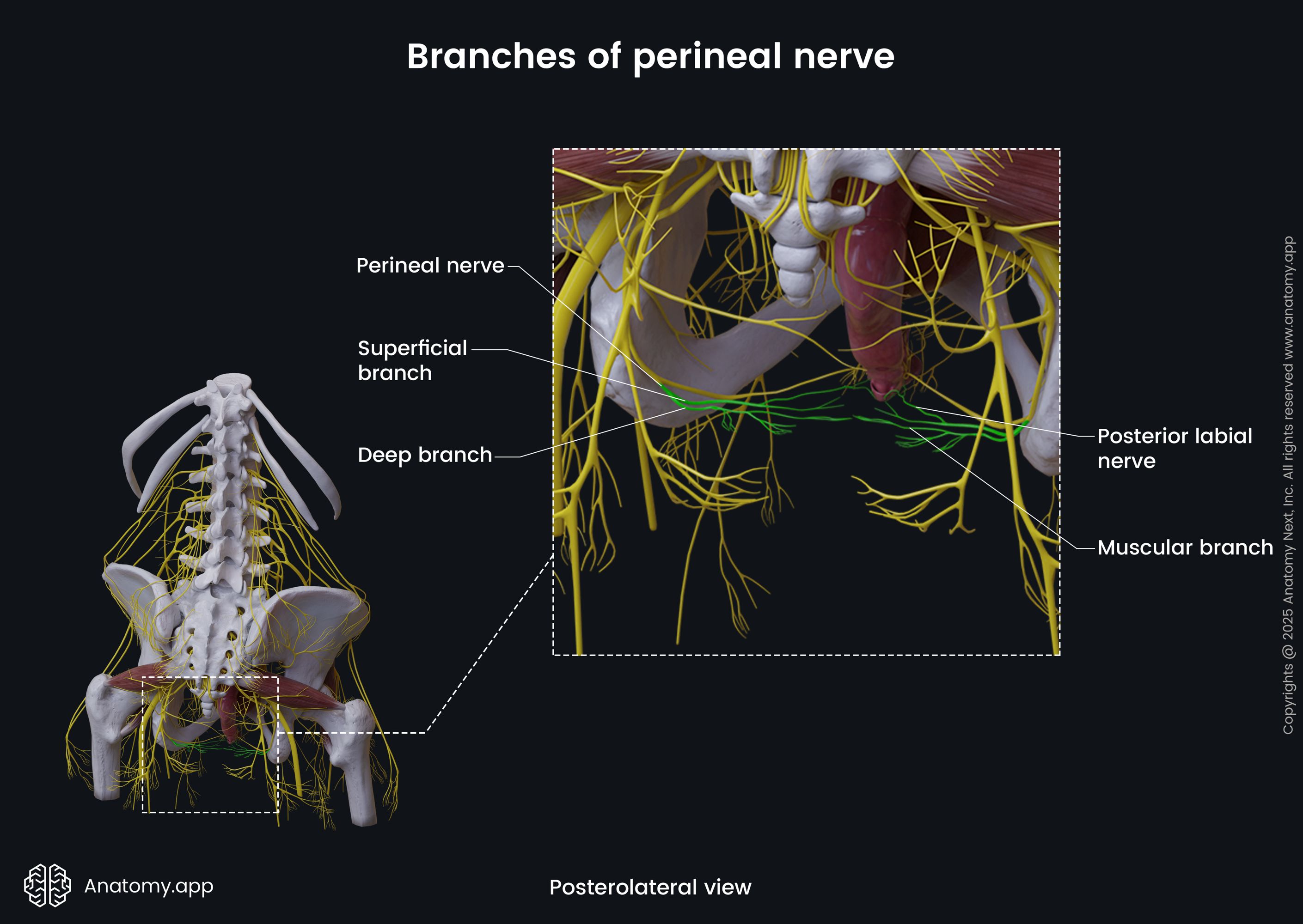
Muscular branches of the perineal nerve innervate the superficial transverse perinei, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus, and deep transverse perinei.