- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
-
Skeleton of upper limb
- Bones of shoulder girdle
- Humerus
- Bones of forearm
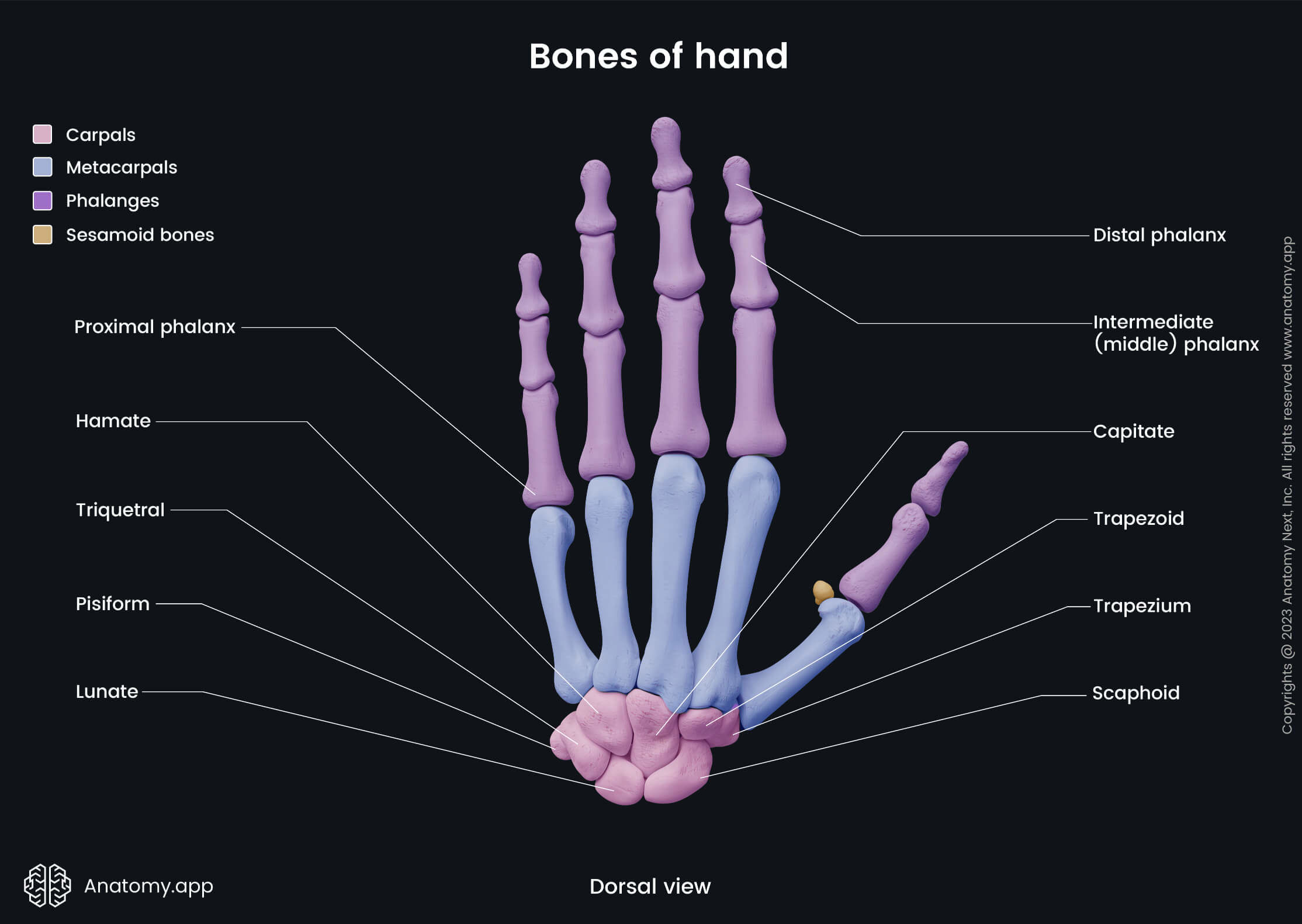
- Bones of hand
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Metacarpal bones
The metacarpal bones (Latin: ossa metacarpi) are also known as the metacarpals. They are five bones that form the middle part of the skeleton of the hand. These bones lie between the proximally located carpal bones and distally positioned phalanges. The metacarpal bones are analogous to the metatarsal bones found in the foot.
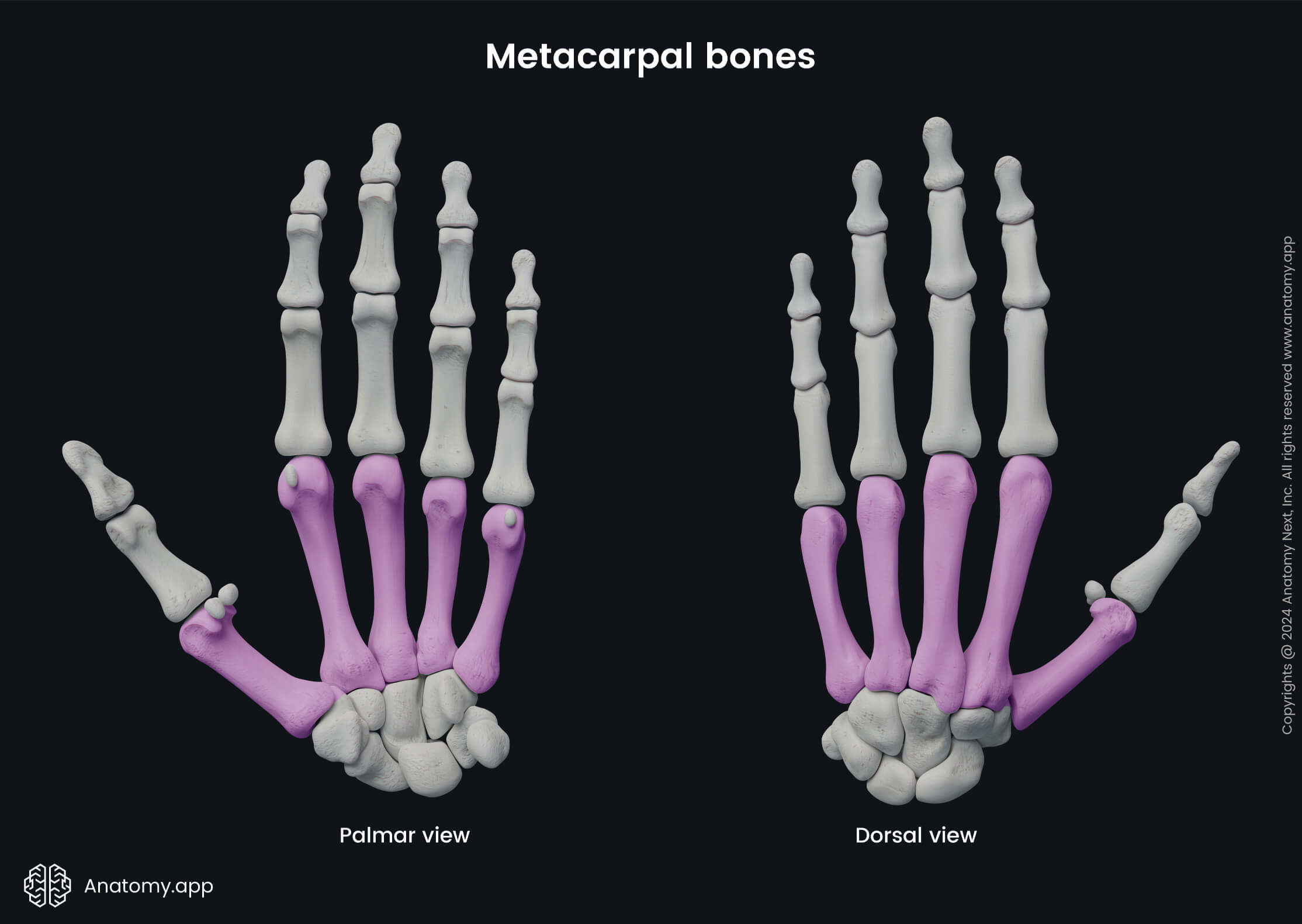
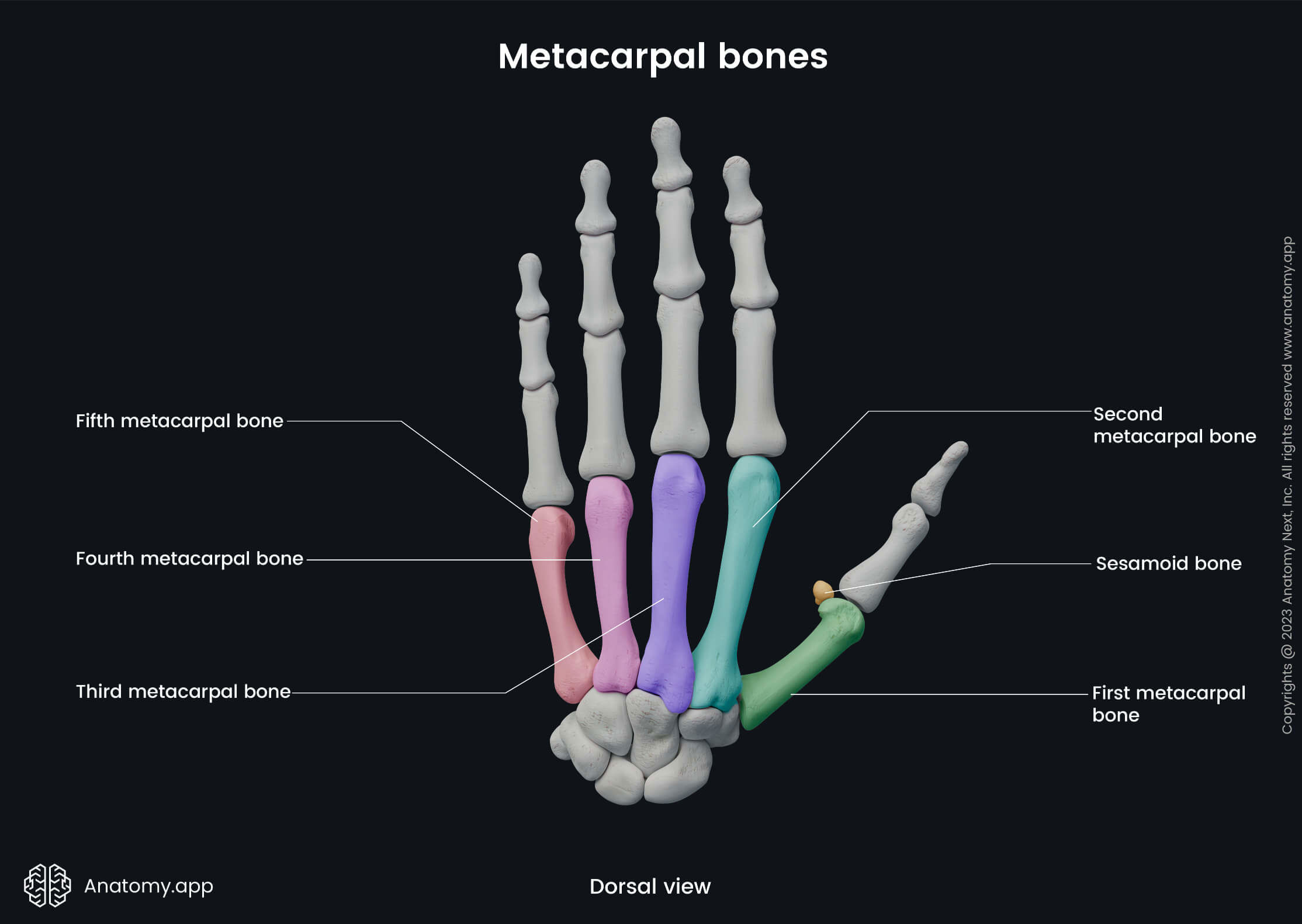
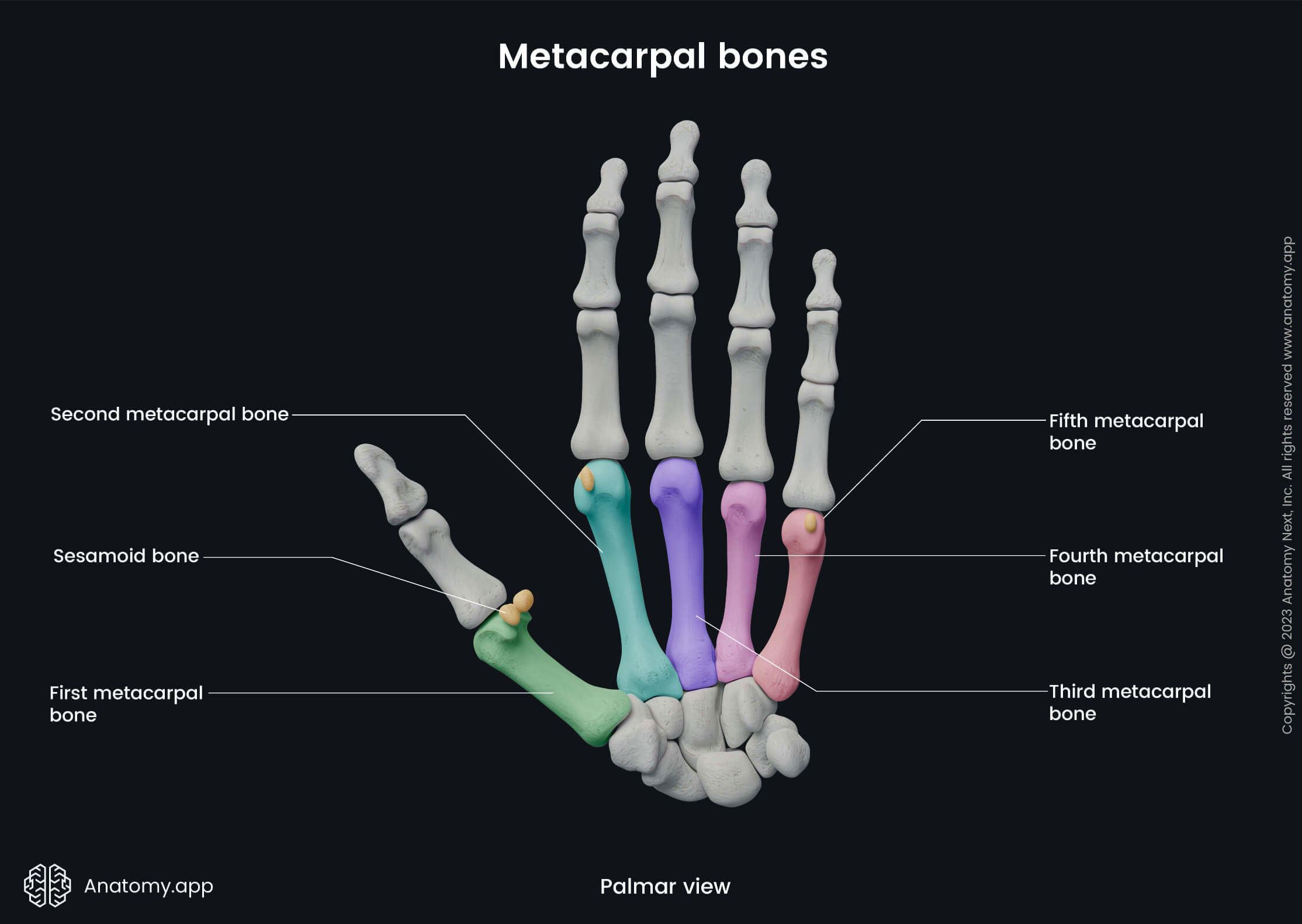
The numbering of five metacarpal bones starts from the radial to the ulnar side of the hand, and each metacarpal bone is associated with a specific finger:
- First metacarpal or metacarpal I - associated with a thumb;
- Second metacarpal (II) - with an index finger;
- Third metacarpal (III) - associated with a middle finger;
- Fourth metacarpal (IV) - with a ring finger;
- Fifth metacarpal (V) - associated with a little finger.
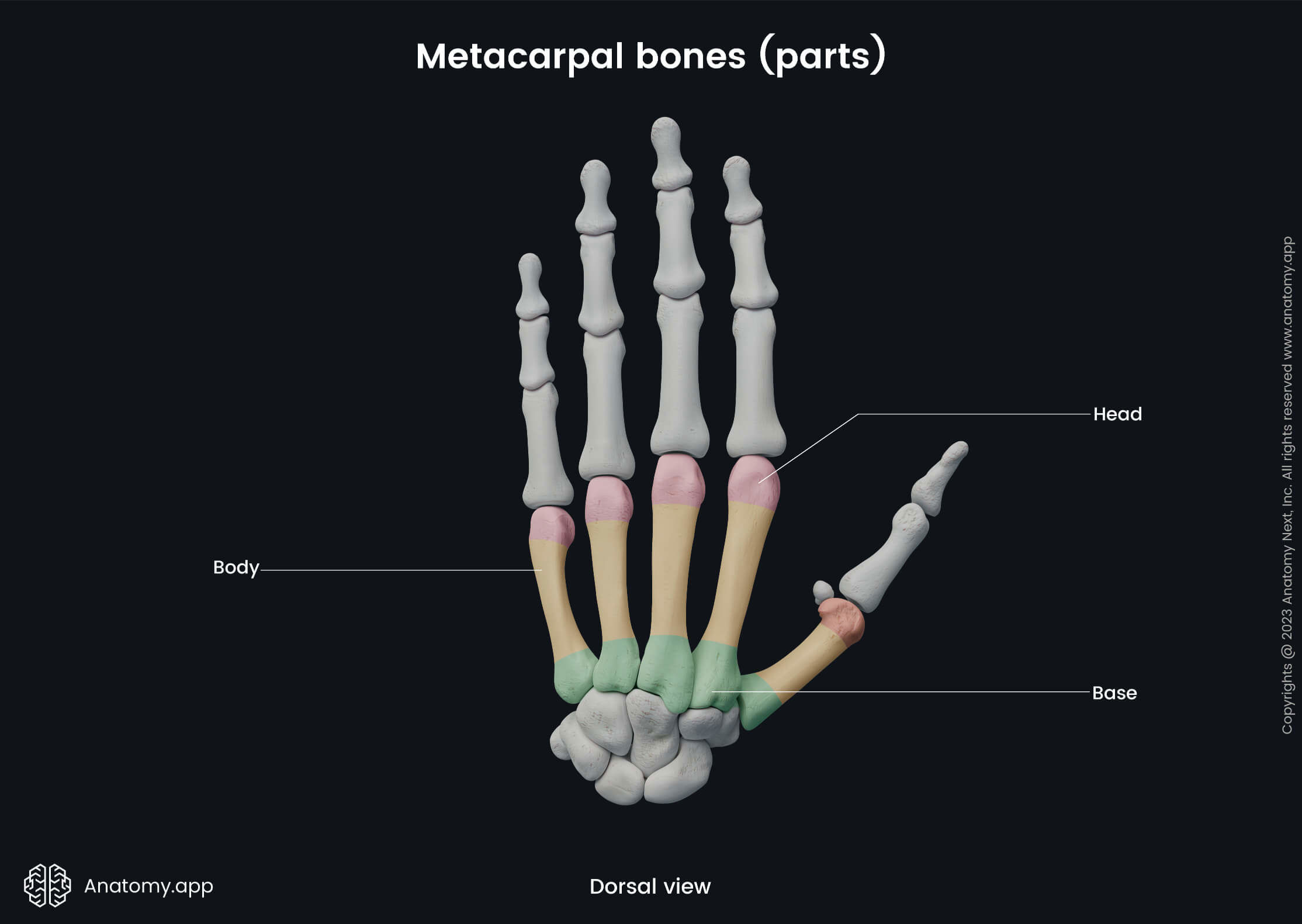
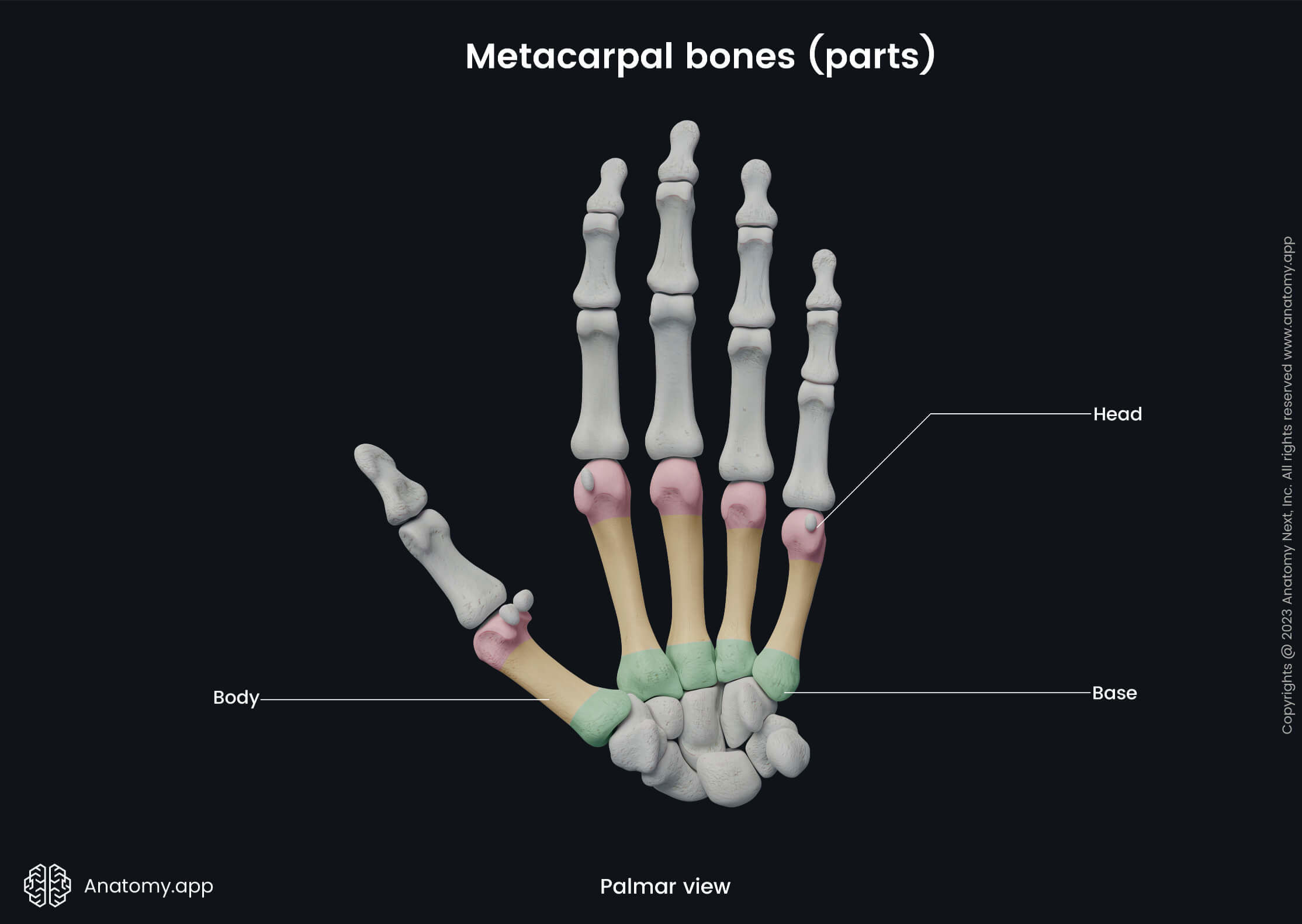
Parts of metacarpal bones
Between two metacarpal bones is present a space called the interosseous metacarpal space. Each metacarpal bone consists of three main parts:
- Base - at the proximal end;
- Body or shaft - the middle part of each bone;
- Head - at the distal end.
Base
The base of each metacarpal bone appears cuboid-shaped, and it is broader on the dorsal surface than on the palmar surface. The base articulates with the carpal bones and with the bases of adjacent metacarpal bones. The dorsal and palmar surfaces of bases are rough and serve as attachment sites for ligaments.
Body
The body or shaft appears prismoid-shaped and slightly curved. It is concave on the dorsal surface while convex on the palmar surface. The body has three surfaces - medial, lateral and dorsal surfaces.
The medial and lateral surfaces of the body appear concave, and they contain longitudinally oriented concavities. These mentioned concavities serve as attachment sites for the palmar interossei muscles.
The dorsal surface in its distal two-thirds is smooth and covered by tendons of the extensor muscles. The dorsal interossei muscles are attached to two sloping surfaces separated by a ridge.
Head
The head presents with an oblong articular surface that articulates with the base of the proximal phalanx. Each side of the head contains a tubercle that serves as an attachment site for the collateral ligament of the metacarpophalangeal joint.
The dorsal surface of the head is broad and flat, and it serves as an attachment site for the tendons of the extensor muscles. The palmar surface of the head in the middle of it contains a groove for the passage of the flexor tendons.
Articulations of metacarpal bones
All metacarpal bones at their distal ends articulate with the proximal phalanges of each finger, forming the metacarpophalangeal joints. Proximally, the metacarpal bones also form articulations known as the carpometacarpal joints between the bases of the metacarpal bones and proximal aspects of carpal bones. In these joints articulate the following metacarpal bones with adjacent carpal bones:
- Metacarpal I forms an articulation with the trapezium bone.
- Metacarpal II articulates with the trapezium, trapezoid and capitate bones.
- Metacarpal III forms a joint together with the capitate bone.
- Metacarpal IV articulates with the hamate bone.
- Metacarpal V forms an articulation with the hamate bone.