- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Muscles of pectoral girdle
- Muscles of shoulder region
- Muscles of upper arm
- Muscles of forearm
- Anterior compartment
- Lateral compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Muscles of hand
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
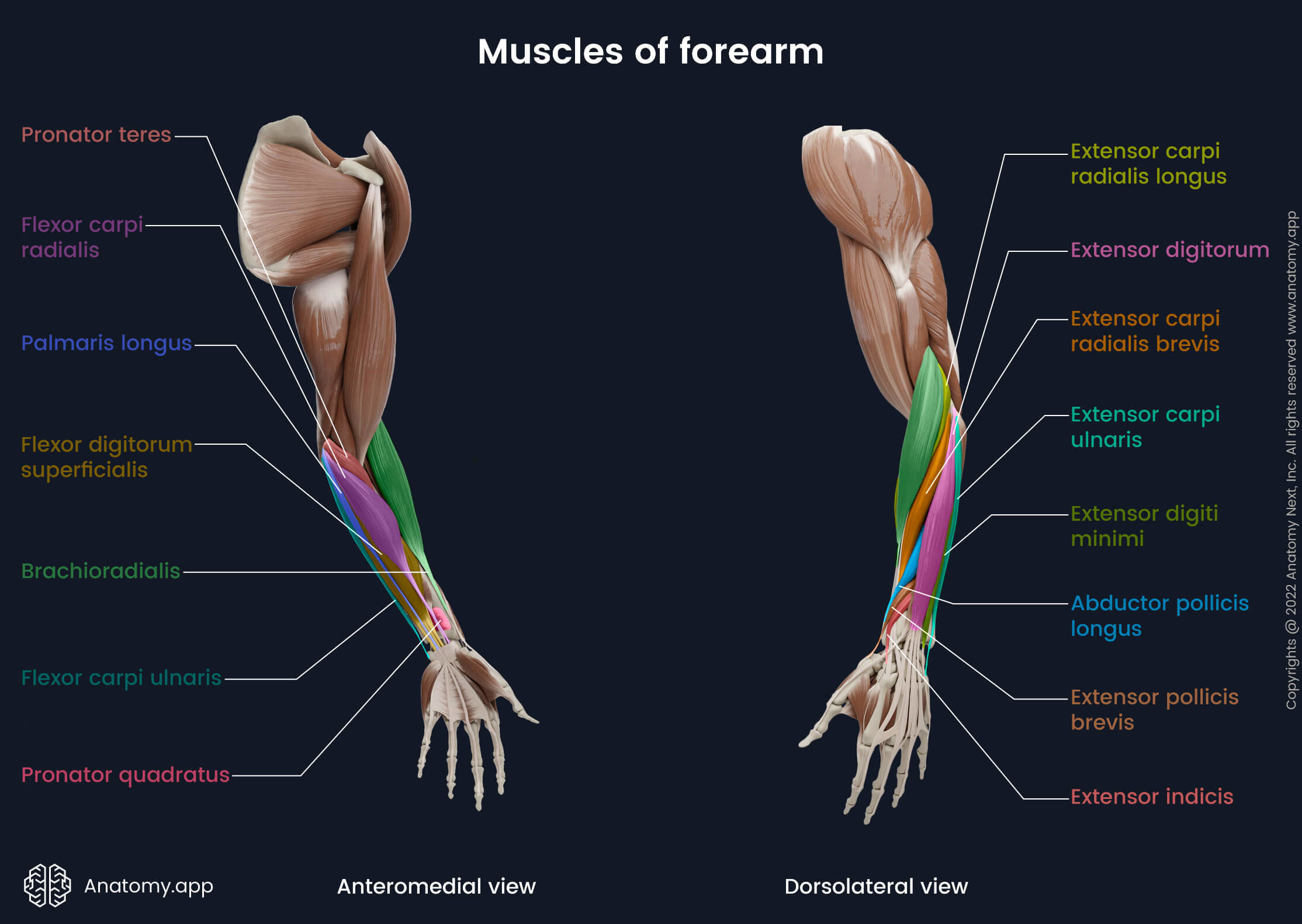
Flexor carpi ulnaris
The flexor carpi ulnaris (Latin: musculus flexor carpi ulnaris) is a long fusiform-shaped superficial muscle of the upper limb that extends between the humerus, ulna, carpal and metacarpal bones. It is one of the wrist flexors, and it belongs to the anterior muscles of the forearm. The flexor carpi ulnaris is situated in the first (superficial) layer of the anterior forearm compartment. Like the pronator teres, this muscle is also composed of two heads - humeral and ulnar.
| Flexor carpi ulnaris | |
| Origin | Humeral head - medial epicondyle of humerus Ulnar head - olecranon, posterior margin of ulna |
| Insertion | Pisiform and hamate bones, base of 5th metacarpal bone |
| Action | Flexion and adduction of wrist |
| Innervation | Ulnar nerve (C7 - T1) |
| Blood supply | Posterior ulnar recurrent, inferior ulnar collateral and ulnar arteries |
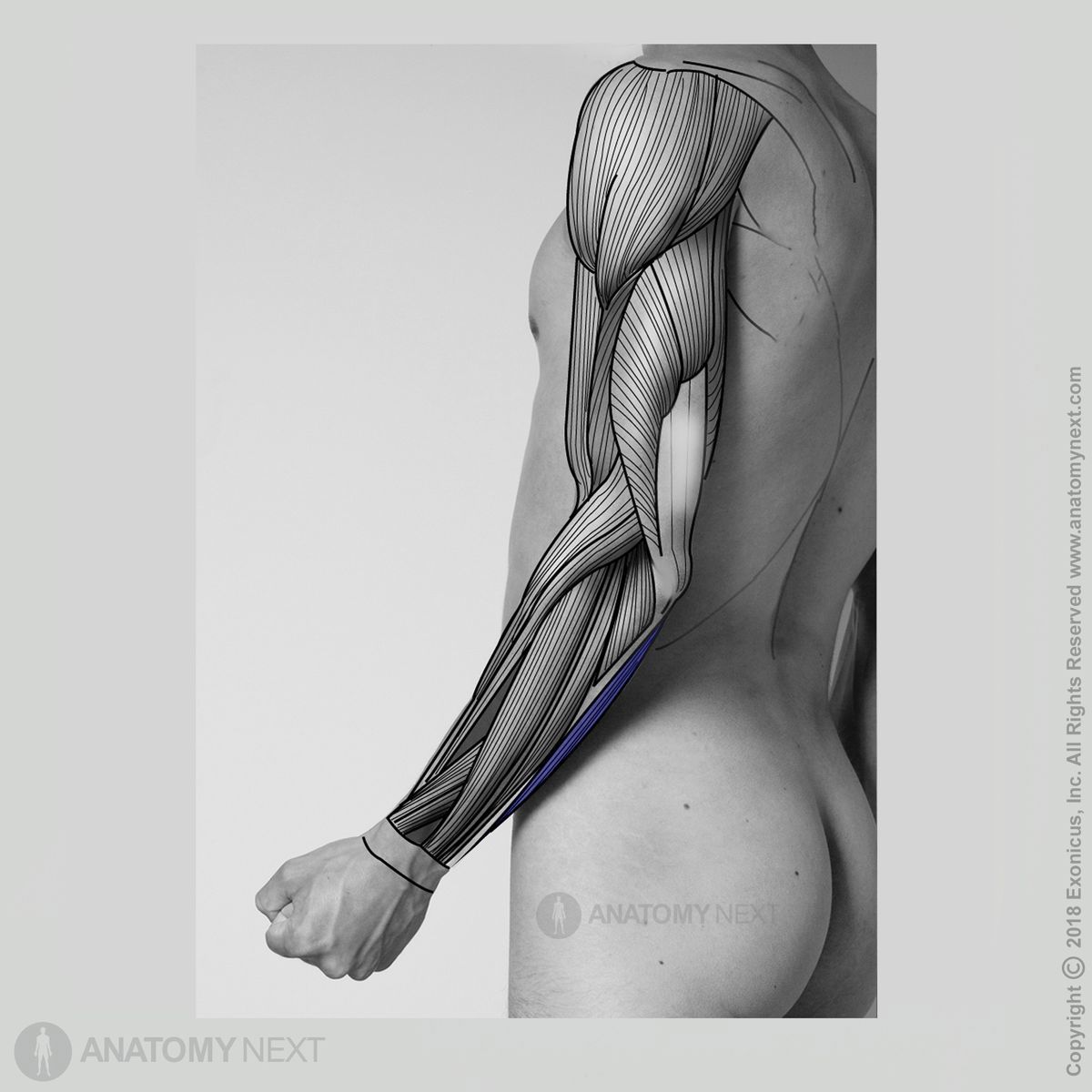
Origin
The humeral head of the flexor carpi ulnaris muscle originates from the medial epicondyle of the humerus. In contrast, the ulnar head arises from the olecranon and proximal posterior margin of the ulna.
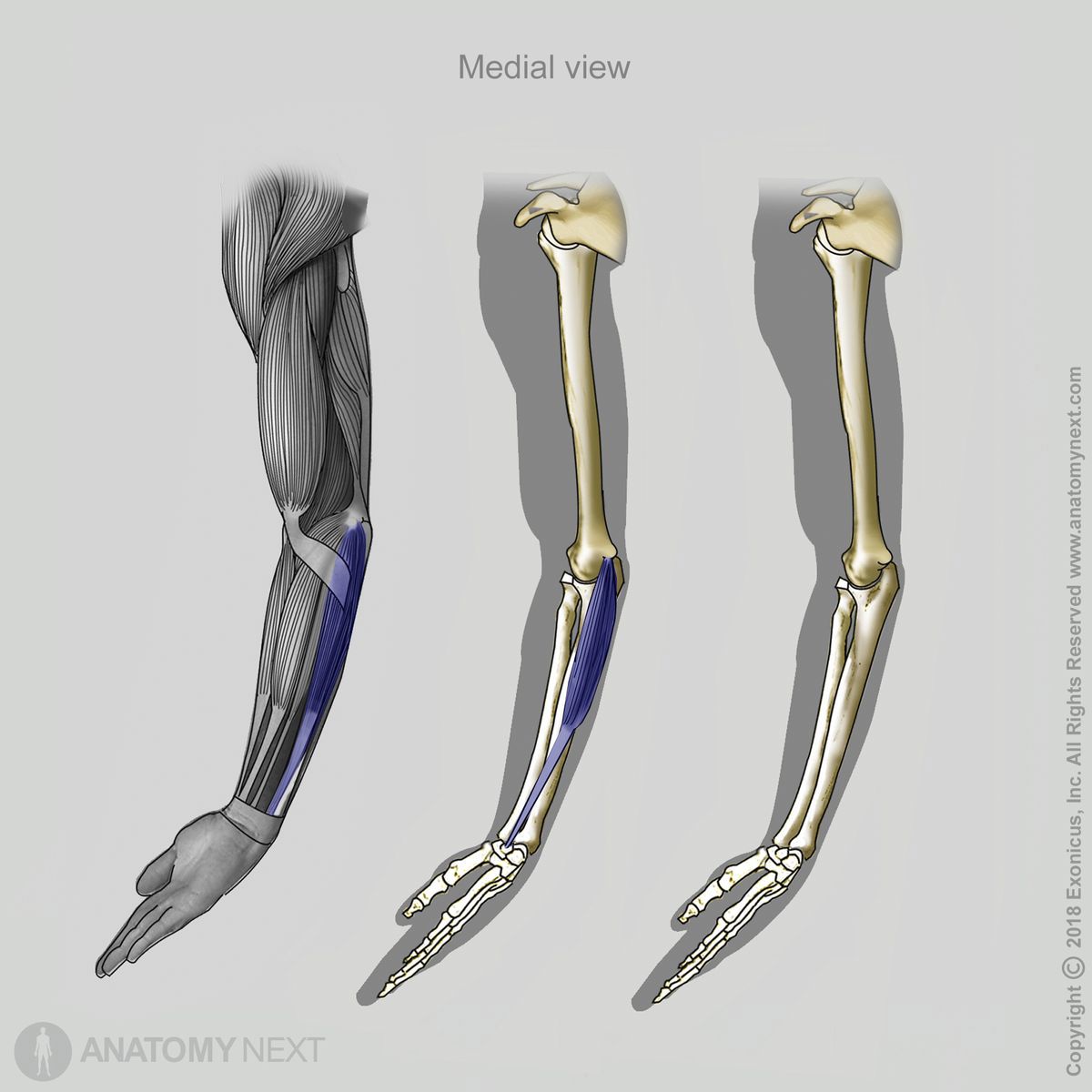
Insertion
The flexor carpi ulnaris inserts on the pisiform and hamate bones and the base of the fifth metacarpal bone.
Action
The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle provides the flexion and adduction of the wrist at the wrist joint.
Innervation
The flexor carpi ulnaris is innervated by the ulnar nerve (C7 - T1) that arises from the brachial plexus.
Blood supply
The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle receives arterial blood supply from the branches of the posterior ulnar recurrent, inferior ulnar collateral and ulnar arteries. The first one is a branch of the ulnar artery, while the rest are branches of the brachial artery.