- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Muscles of pectoral girdle
- Muscles of shoulder region
- Muscles of upper arm
- Muscles of forearm
- Anterior compartment
- Lateral compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Muscles of hand
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
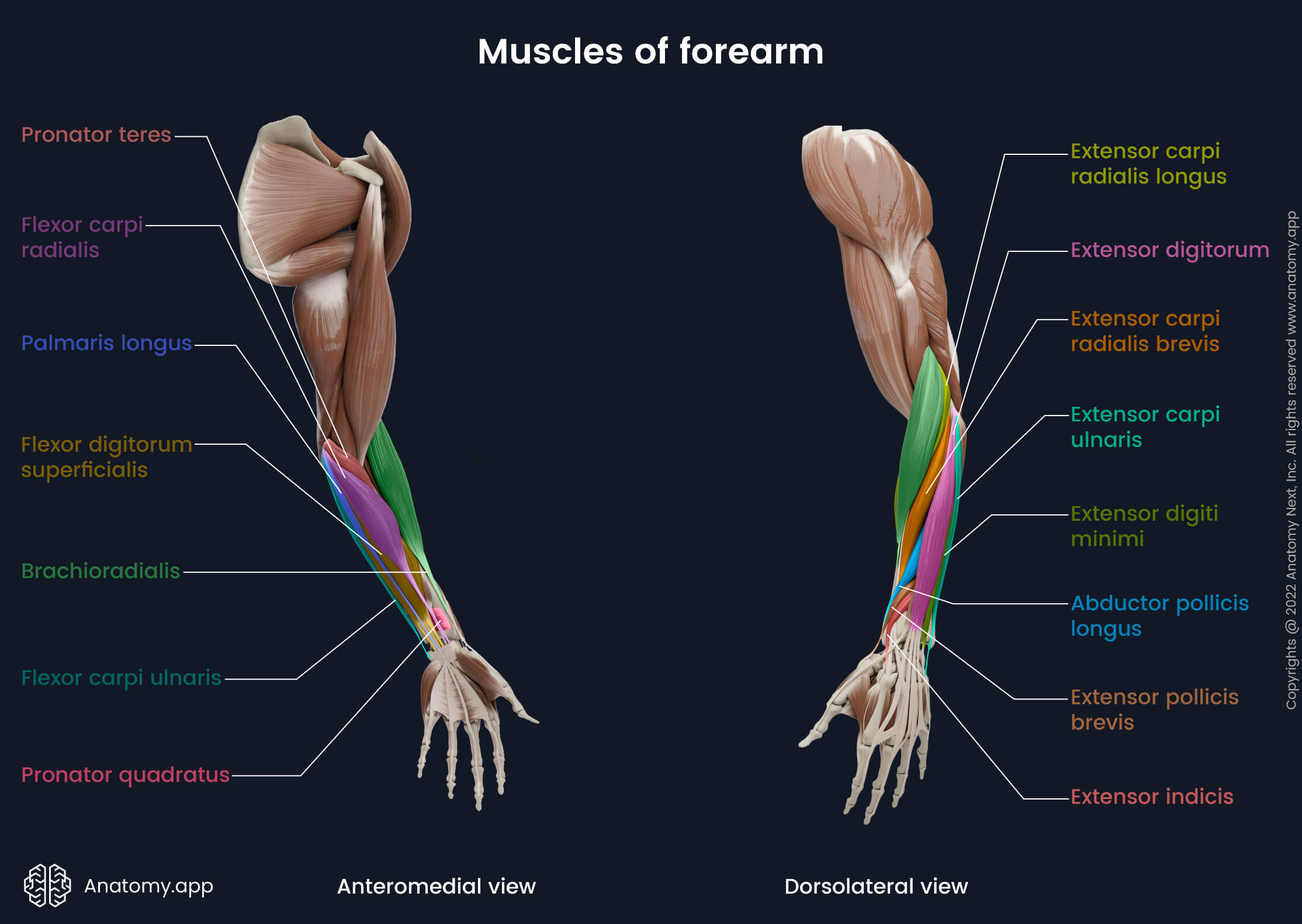
Extensor carpi ulnaris
The extensor carpi ulnaris (Latin: extensor carpi ulnaris) is a fusiform-shaped superficial muscle of the forearm that stretches between the ulna, humerus and fifth metacarpal bone. It belongs to the posterior compartment of the forearm muscles, and, together with the extensor digitorum and extensor digiti minimi muscles, it lies in the first (superficial) layer.
| Extensor carpi ulnaris | |
| Origin | Lateral epicondyle of humerus, posterior margin of ulna, olecranon |
| Insertion | Base of 5th metacarpal bone |
| Action | Extension and adduction of hand |
| Innervation | Posterior interosseous nerve of radial nerve (C7, C8) |
| Blood supply | Posterior interosseous and radial recurrent arteries |
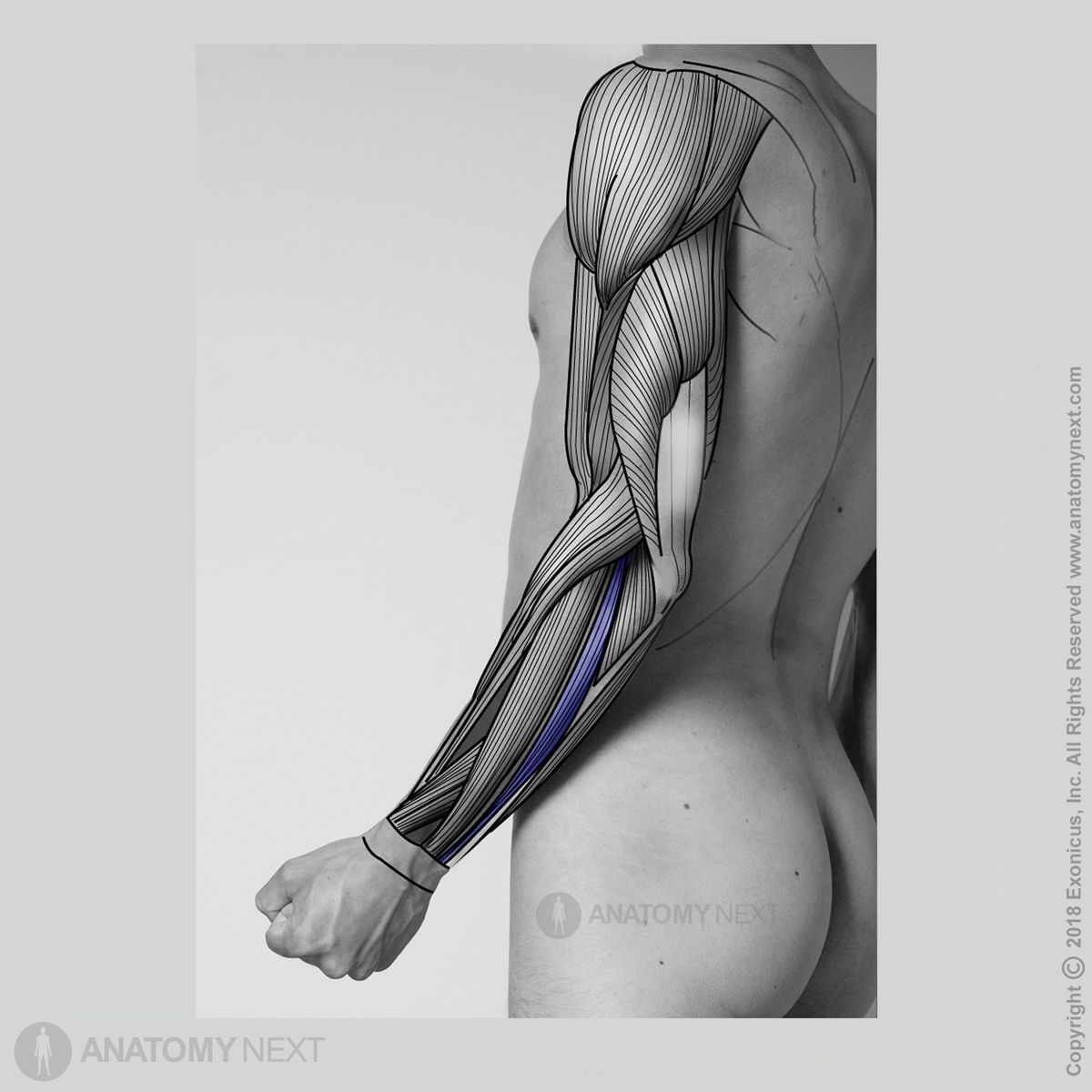
Origin
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle originates from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, posterior margin and olecranon of the ulna.
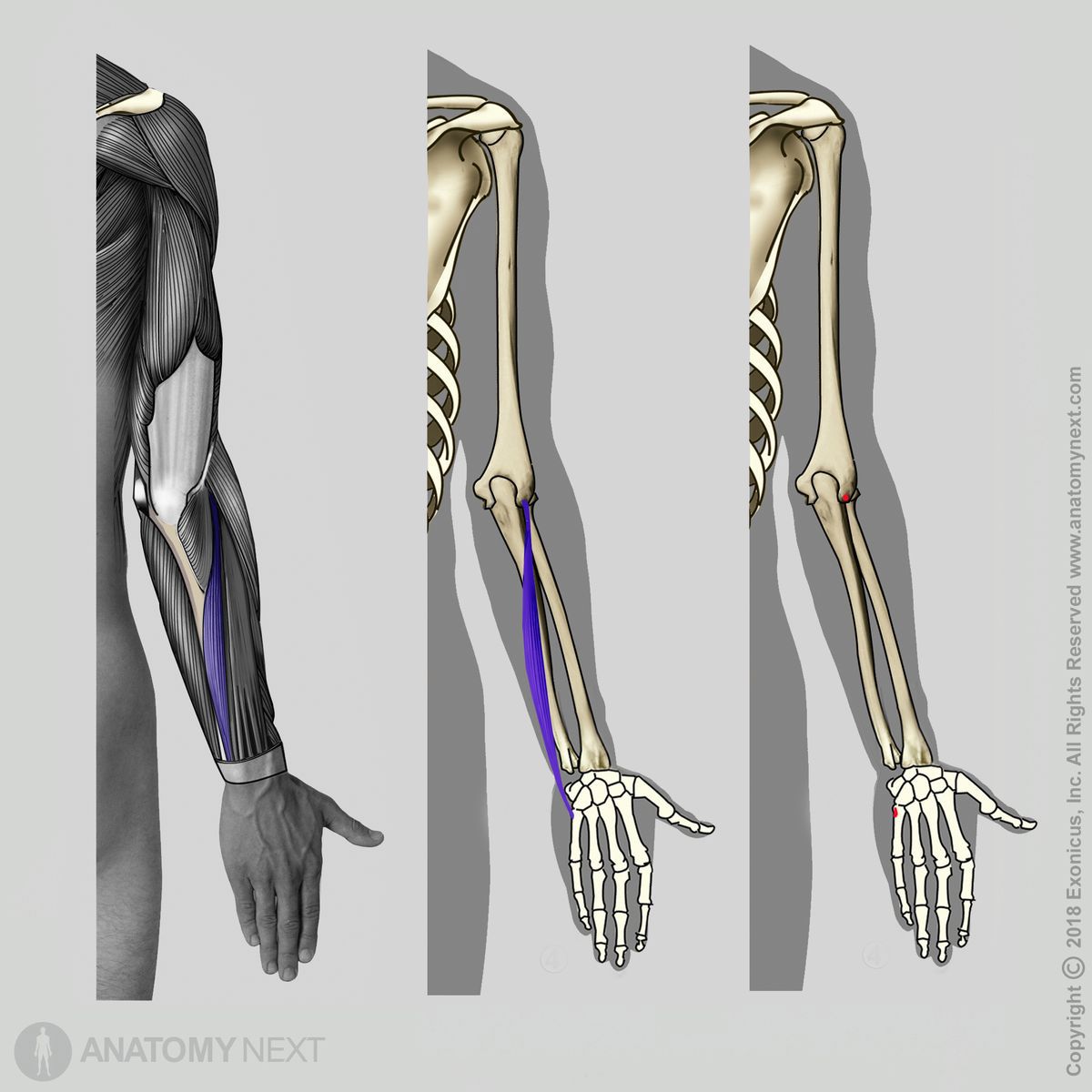
Insertion
The extensor carpi ulnaris inserts on the base of the fifth metacarpal bone.
Action
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle extends and adducts the hand at the wrist joint.
Innervation
The extensor carpi ulnaris is innervated by the posterior interosseous branch of the radial nerve (C7, C8). The radial nerve arises from the brachial plexus.
Blood supply
The extensor carpi ulnaris muscle receives arterial blood supply from the posterior interosseous and radial recurrent arteries. The first one is a branch of the common interosseous artery, while the radial recurrent artery arises from the radial artery.