- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
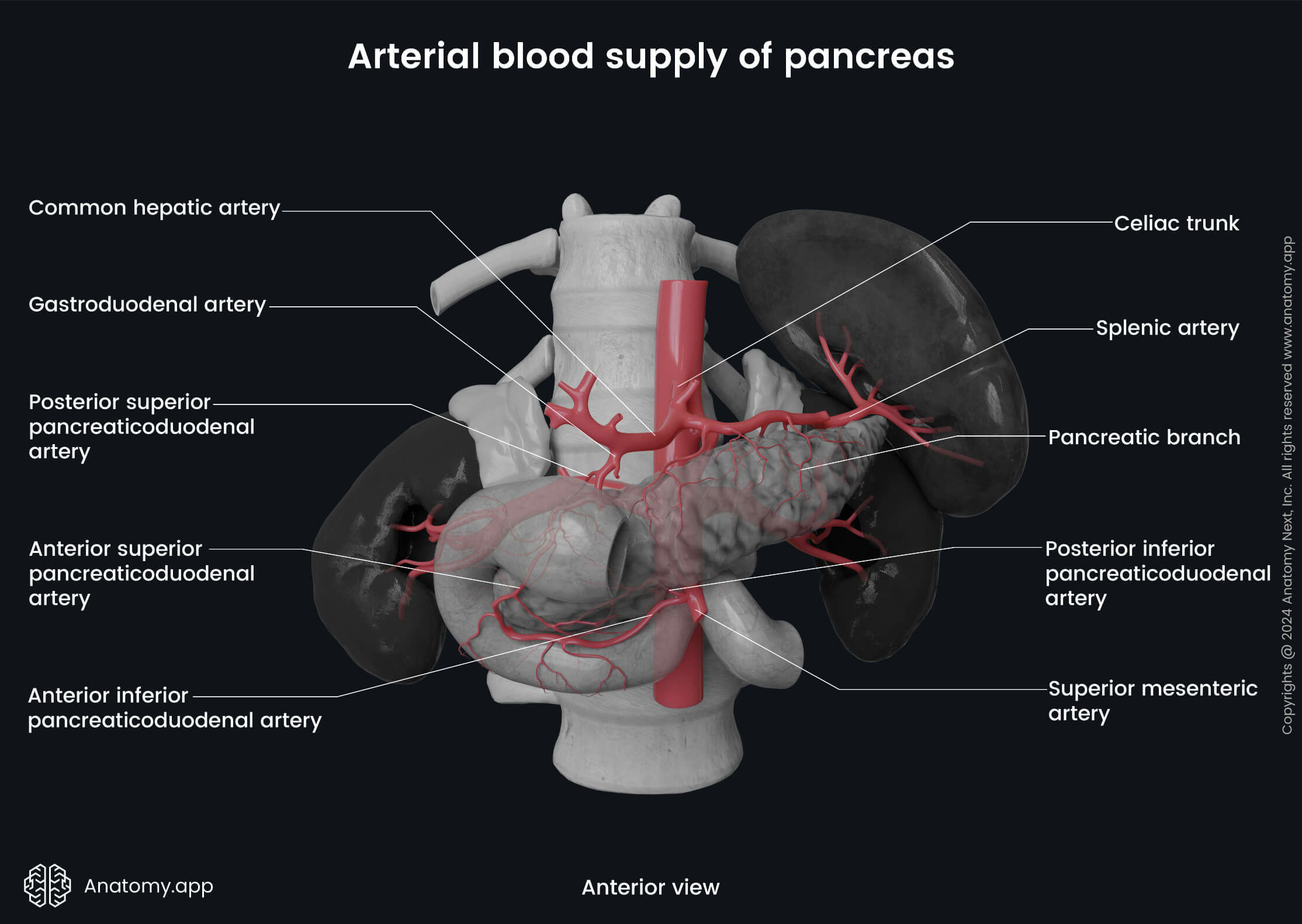
Celiac trunk
The celiac trunk (also known as coeliac trunk, coeliac artery, Latin: truncus coeliacus, arteria coeliaca) is a major visceral branch of the abdominal aorta arising from its anterior side. The celiac trunk supplies the lower esophagus, stomach, superior part of the duodenum, and proximal half of the descending part of the duodenum.
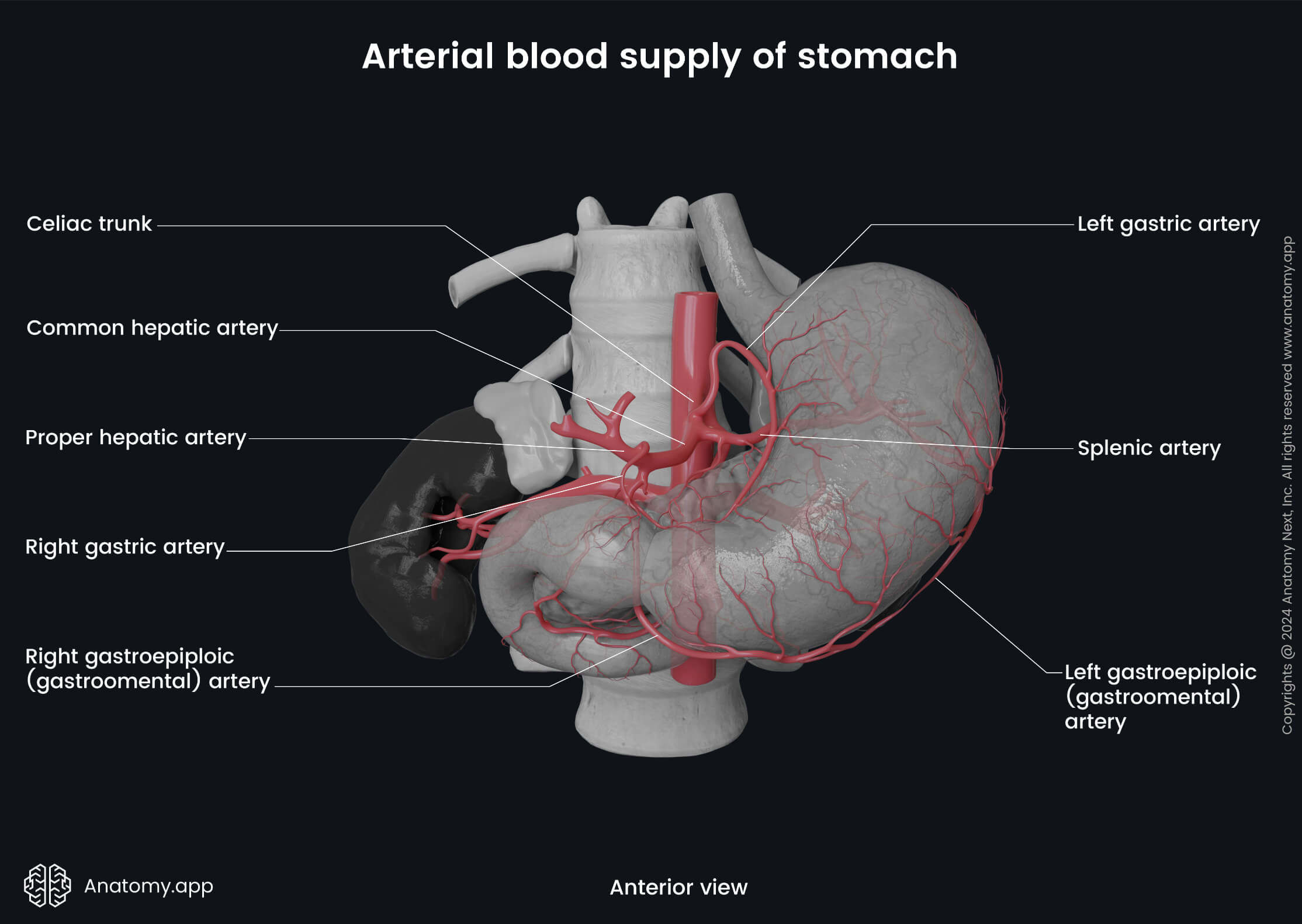
The celiac trunk is an unpaired vessel that starts from the abdominal aorta immediately below the aortic hiatus of the diaphragm. It usually arises anterior to the upper part of the first lumbar vertebra (L1) or at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebra (T2). Then it immediately divides into several branches:
- Left gastric artery - gives off an esophageal branch and a stomach branch;
- Splenic artery - gives rise to the dorsal pancreatic artery, short gastric arteries, left gastro-omental arteries, and greater pancreatic artery;
- Common hepatic artery - gives rise to the proper hepatic artery, right gastric artery, and the gastroduodenal artery;
- Additionally, the celiac artery may also give rise to the inferior phrenic arteries.