- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
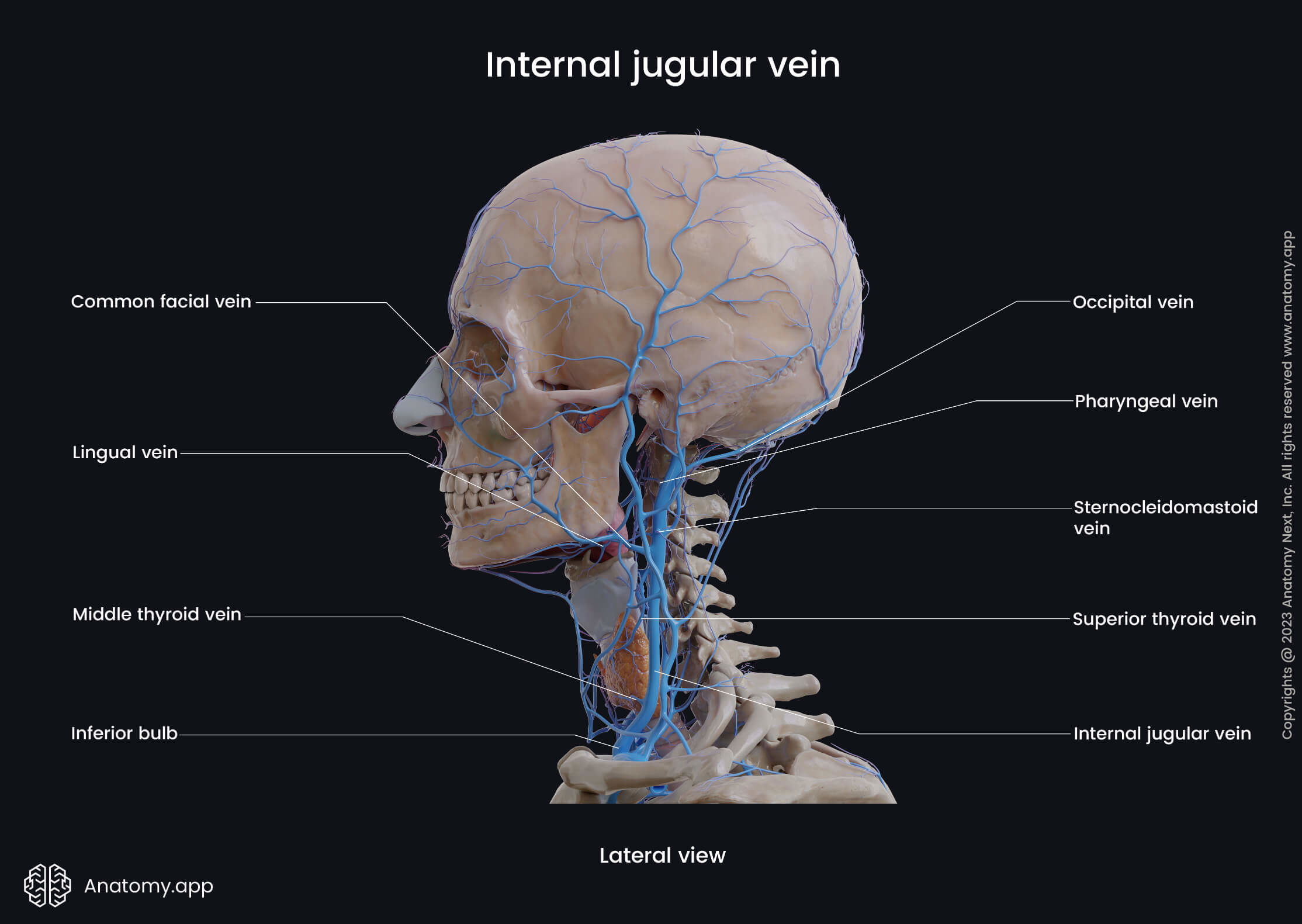
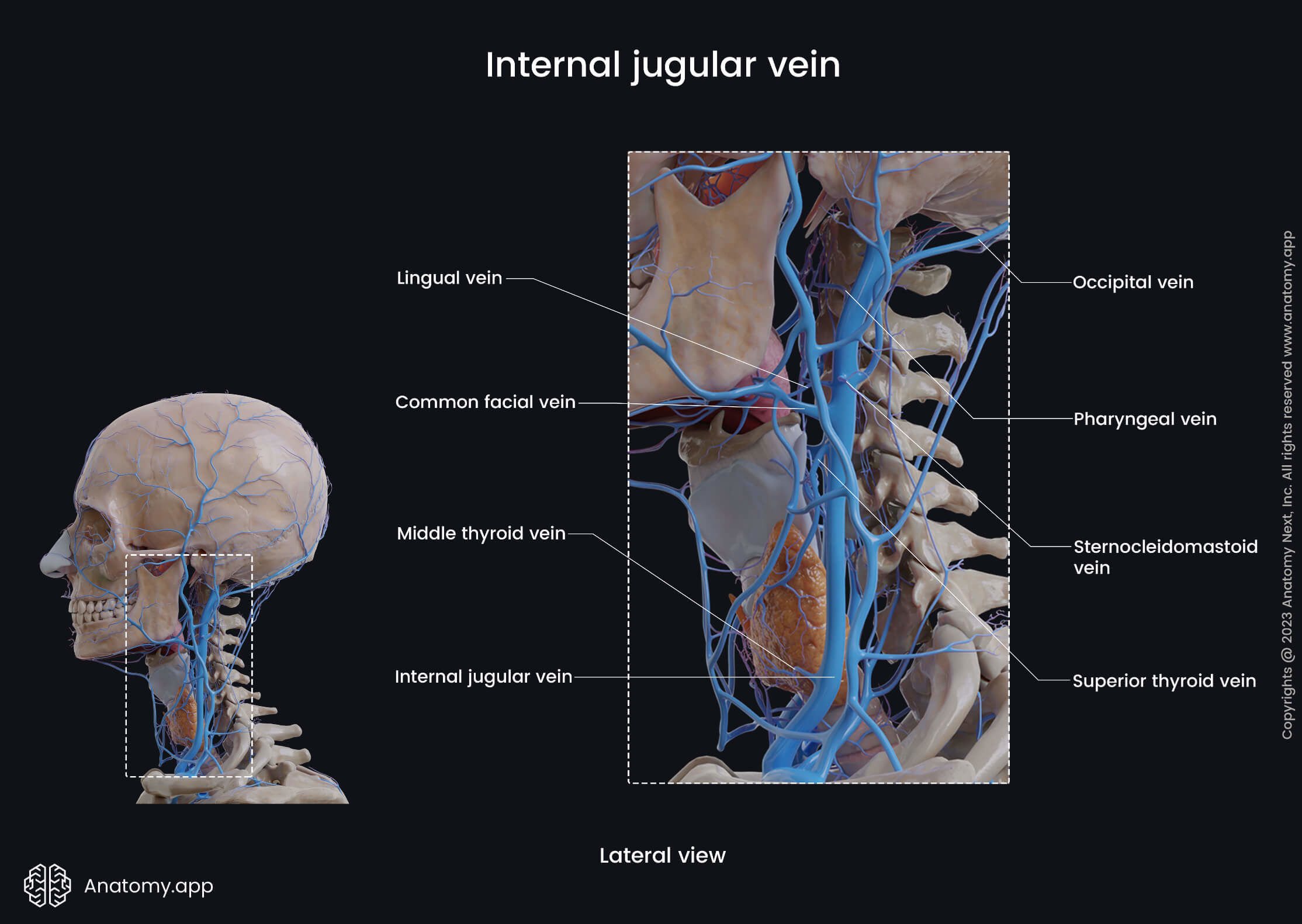
Internal jugular vein
The internal jugular vein (Latin: vena jugularis interna) is a blood vessel that arises from the junction of two intracranial venous sinuses - the inferior petrosal sinus and the sigmoid sinus. The internal jugular vein collects venous blood from the brain, skull, and superficial parts of the face and neck.
The internal jugular vein arises at the cranial base in the jugular foramen. Further, the vein passes inferiorly within the carotid sheath situated anterolateral to the common carotid artery. At the level of the sternoclavicular joint, the internal jugular vein unites with the subclavian vein to form the brachiocephalic vein. On its course, the internal jugular vein receives several tributaries, including:
- Inferior petrosal sinus
- Pharyngeal veins
- Common facial vein
- Lingual vein
- Superior thyroid vein
- Middle thyroid vein
- Occipital vein