Platysma
The platysma is a wide and flat sheet-like muscle located in the anterior compartment of the neck right below the skin. It is surrounded by the superficial cervical fascia. The platysma is a paired thin superficial neck muscle that extends between the upper aspect of the thorax and shoulders and the lower aspect of the face.
The platysma arises from the fascia that covers the clavicle, the acromial region and the superior aspects of the deltoid muscle and pectoralis major muscle. Further, the muscle fibers ascend on the anterolateral side of the neck toward the mandible, going along the neck in the superomedial direction. However, they usually do not extend to the midline of the neck, or only a few fibers connect with the fibers of the opposite muscle.
The platysma has several insertion sites. It inserts onto the lower border of the body of the mandible and the skin of the lower lip, as well as blends in the subcutaneous tissue and skin of the region around the mouth. Also, it blends with the muscles surrounding the mouth, such as the depressor anguli oris muscle, orbicularis oris muscle and depressor labii inferioris muscle. Moreover, the platysma participates in the formation of the modiolus of angulus oris.
Origin: fascia covering the lower neck and upper anterolateral aspect of the thorax, including the clavicle, acromial region, deltoid muscle and pectoralis major muscle.
Insertion: lower border of the base of the mandible, skin over the lower aspect of the face, angle of the mouth, skin of the lower lip, modiolus; the platysma also blends with the fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle, depressor anguli oris muscle and depressor labii inferioris muscle.
Action: tenses the skin of the lower aspect of the face and anterior aspect of the neck; it also contributes to the depression of the mandible and angle of the mouth, producing facial expressions of disgust, surprise and horror.
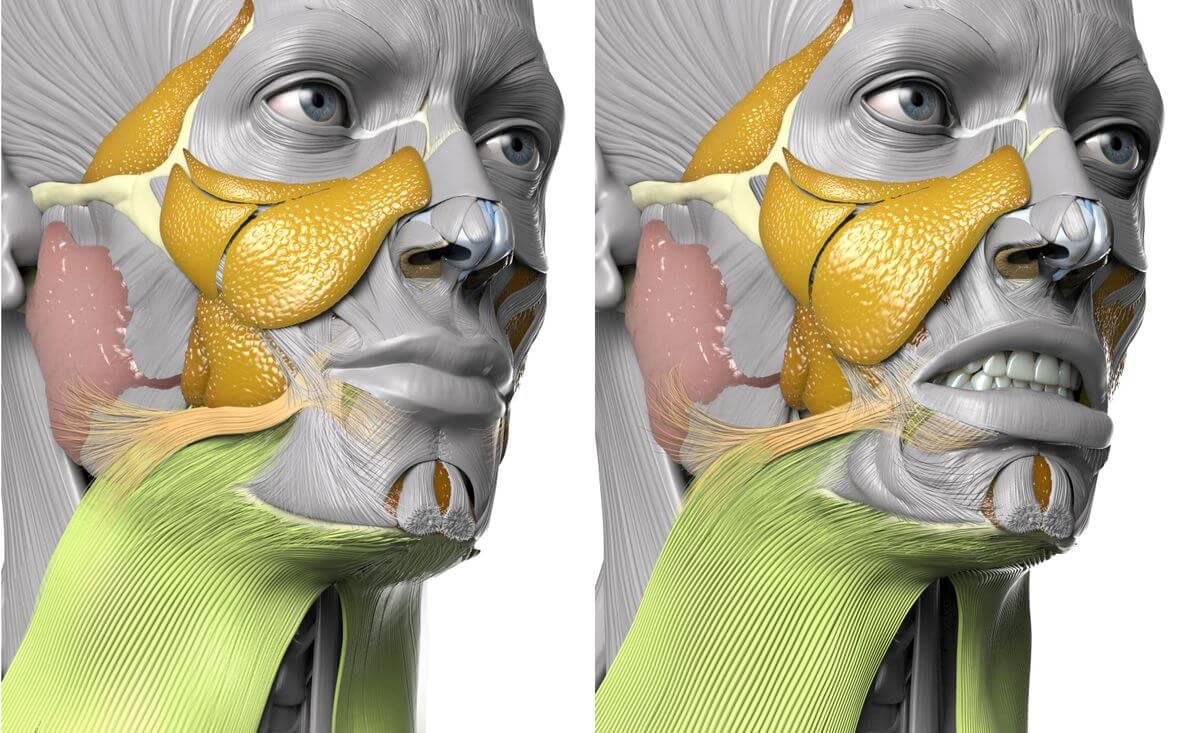
Innervation: cervical branch of the facial nerve (CN VII); may receive some nerve fibers also from the mandibular marginal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply: submental artery (branch of the facial artery), suprascapular artery (arises from the thyrocervical trunk).