- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
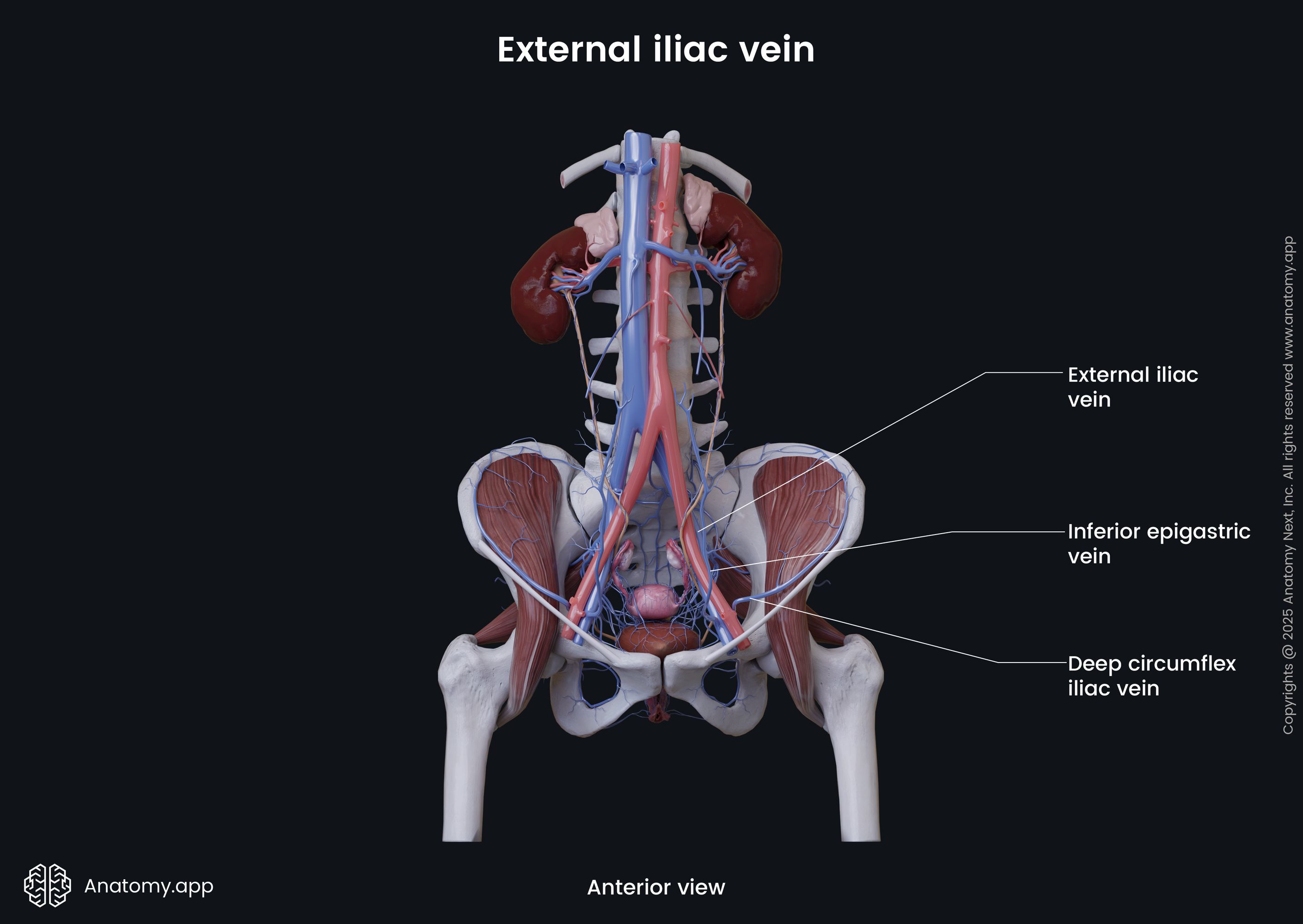
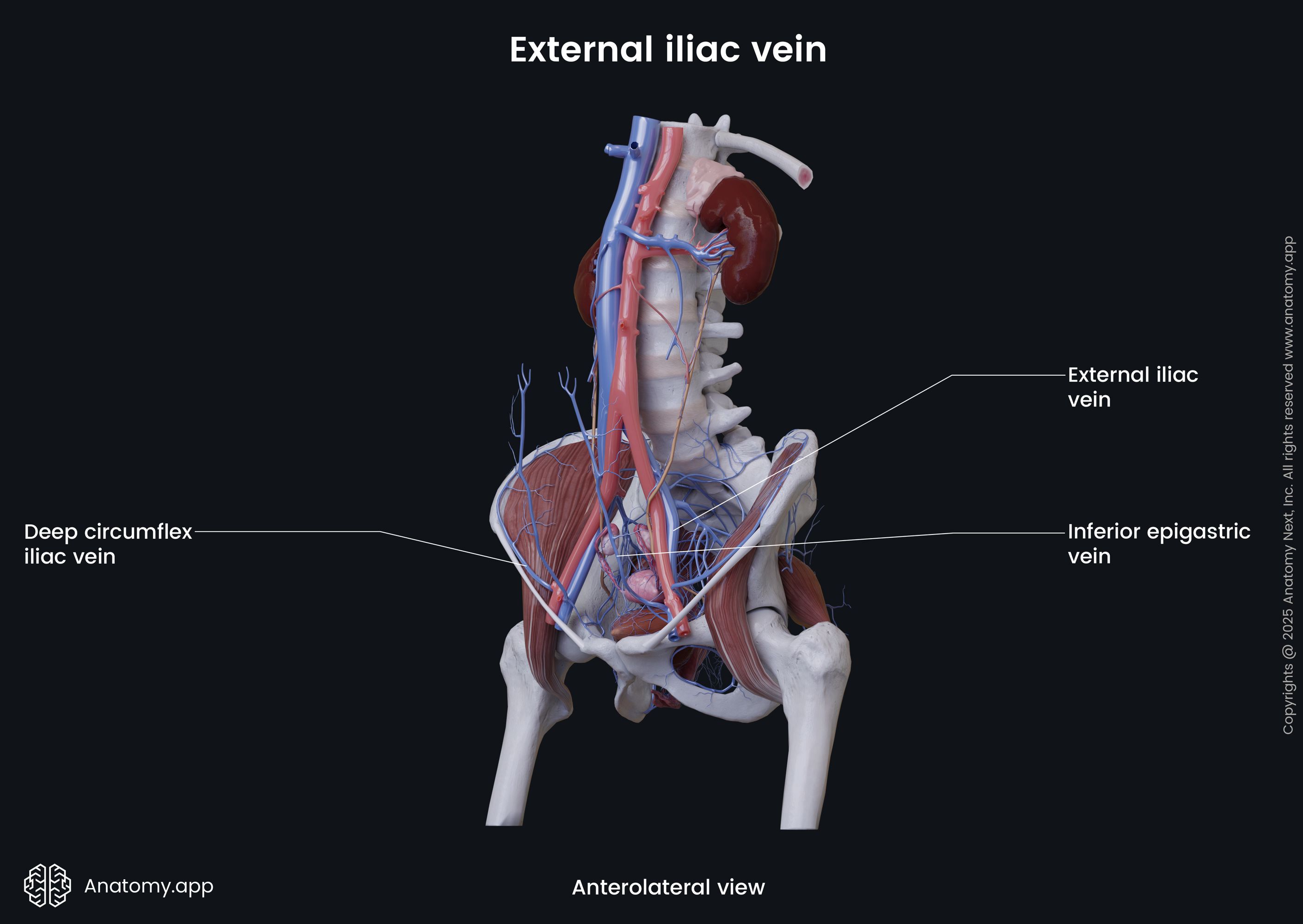
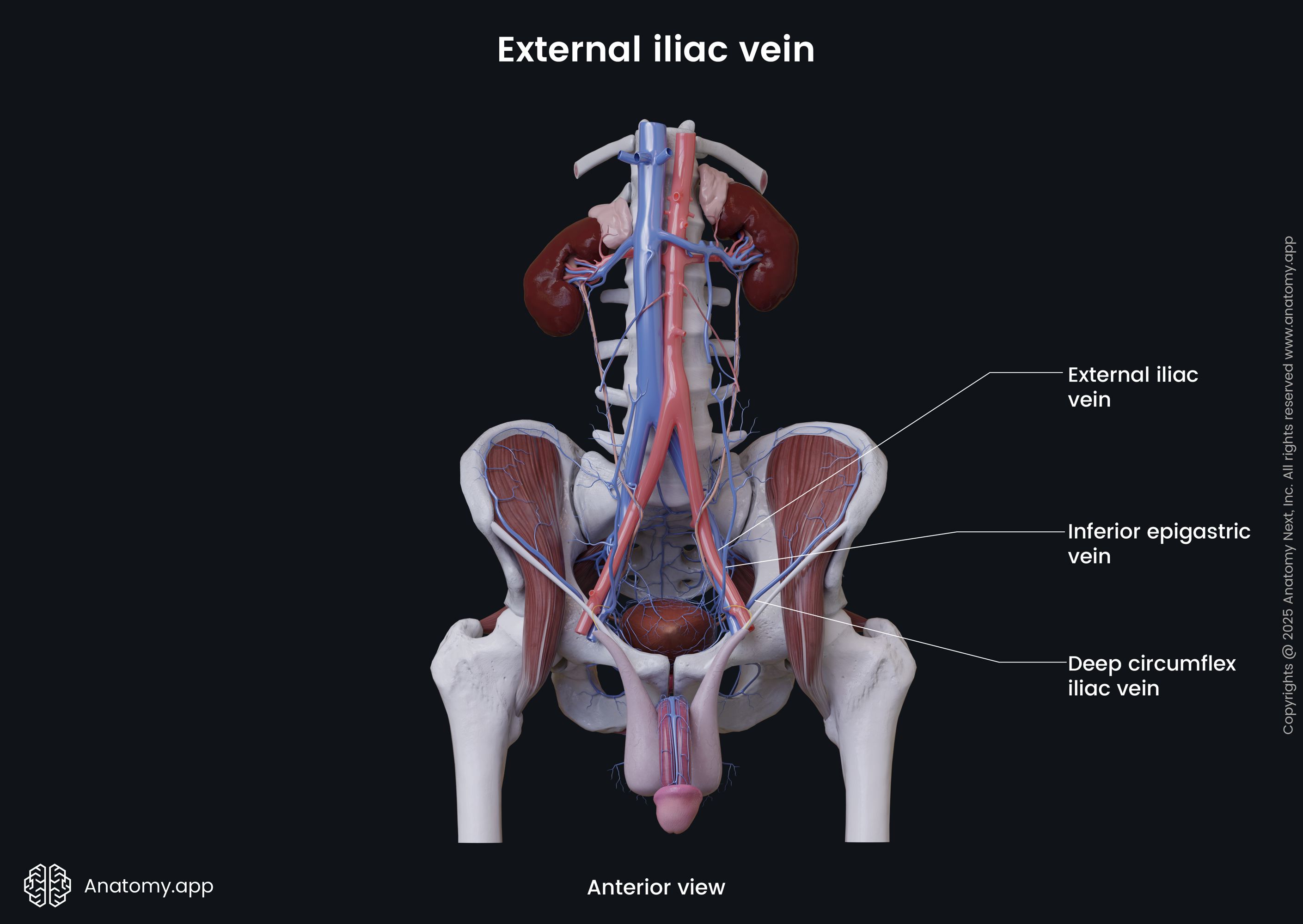
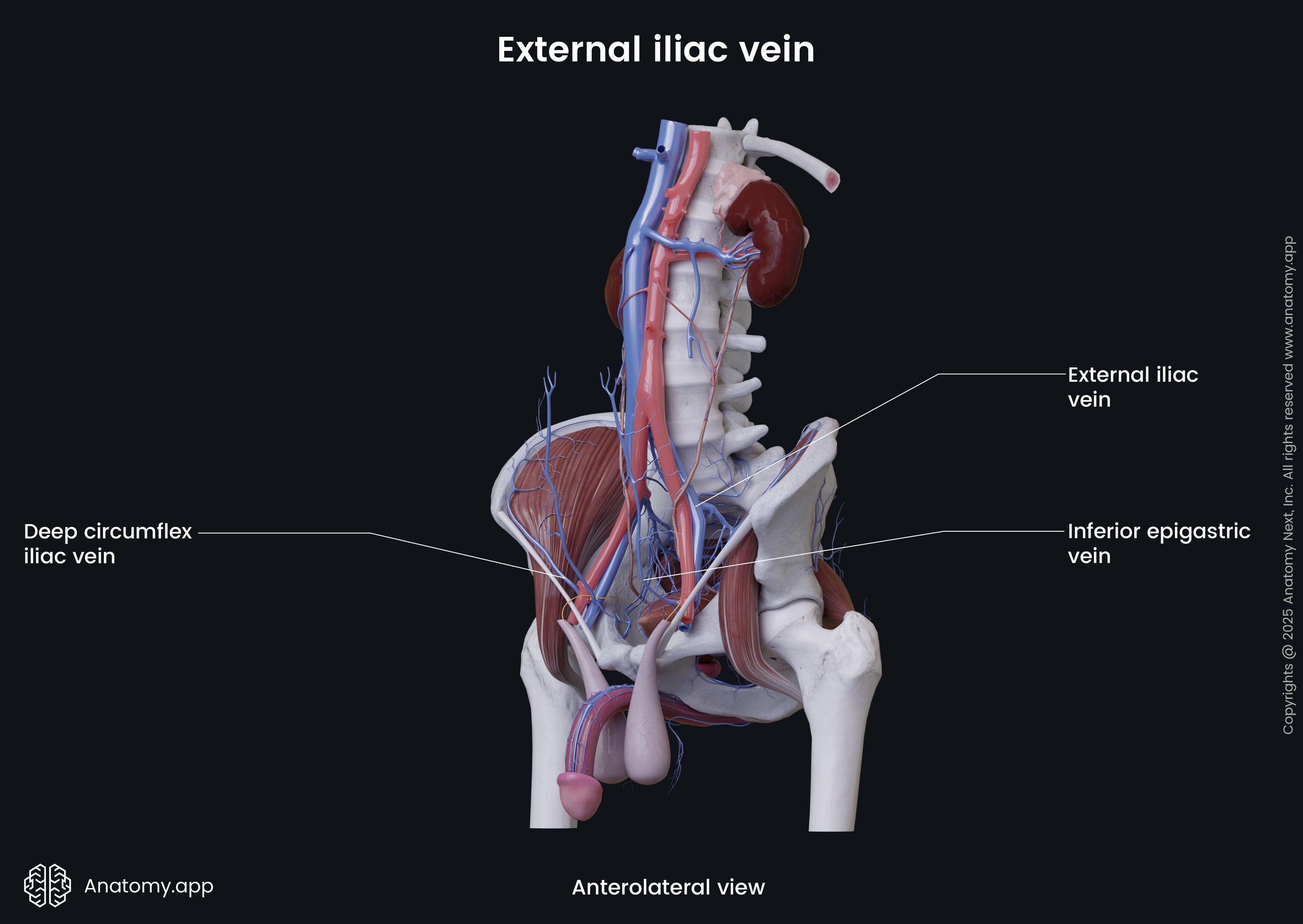
External iliac vein
The external iliac vein (Latin: vena iliaca externa) is a major blood vessel of the pelvis. It is the continuation of the femoral vein, as it reaches the pelvis. The right and left external iliac veins collect deoxygenated blood from muscles and skin in the lower abdominal wall.
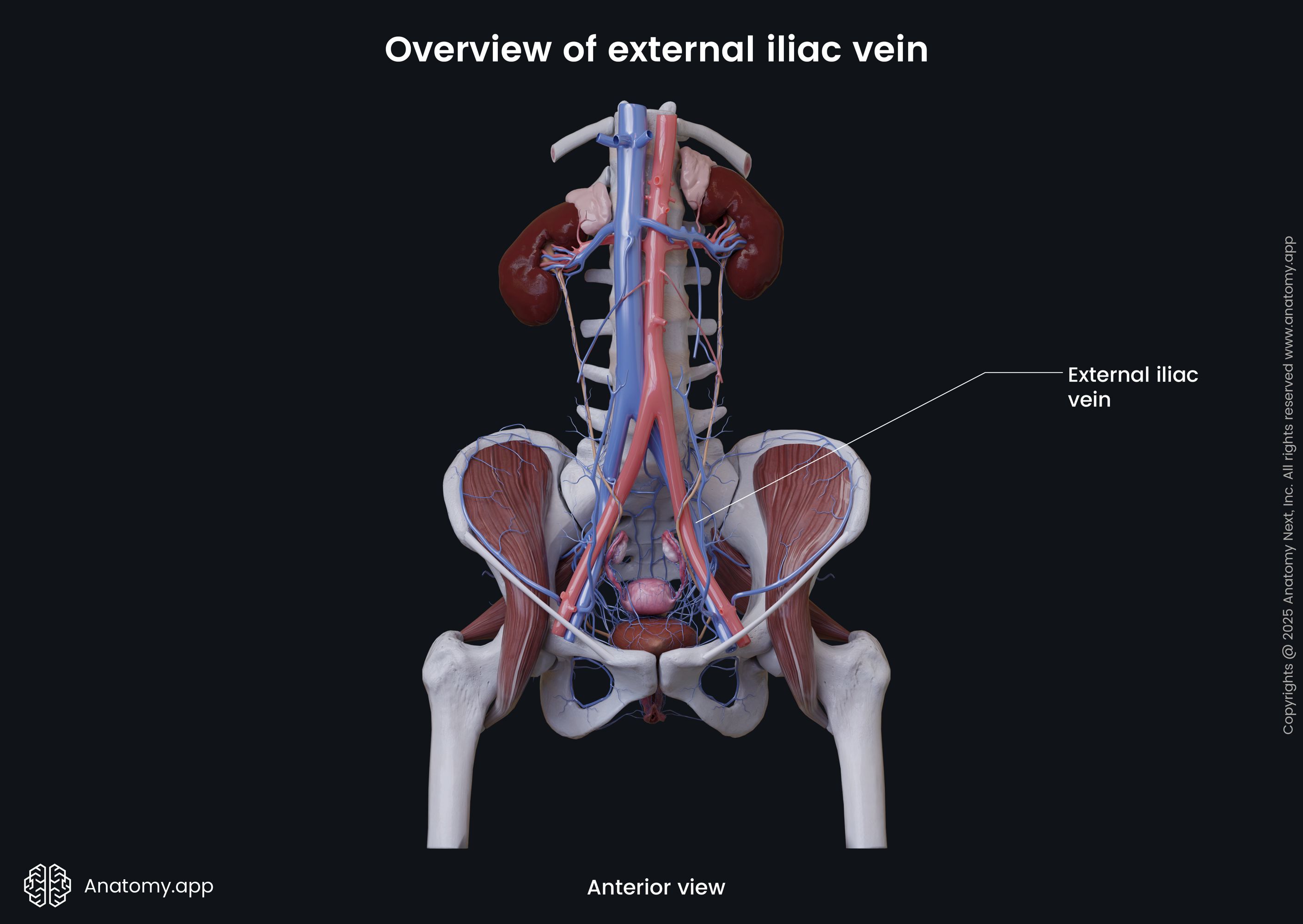
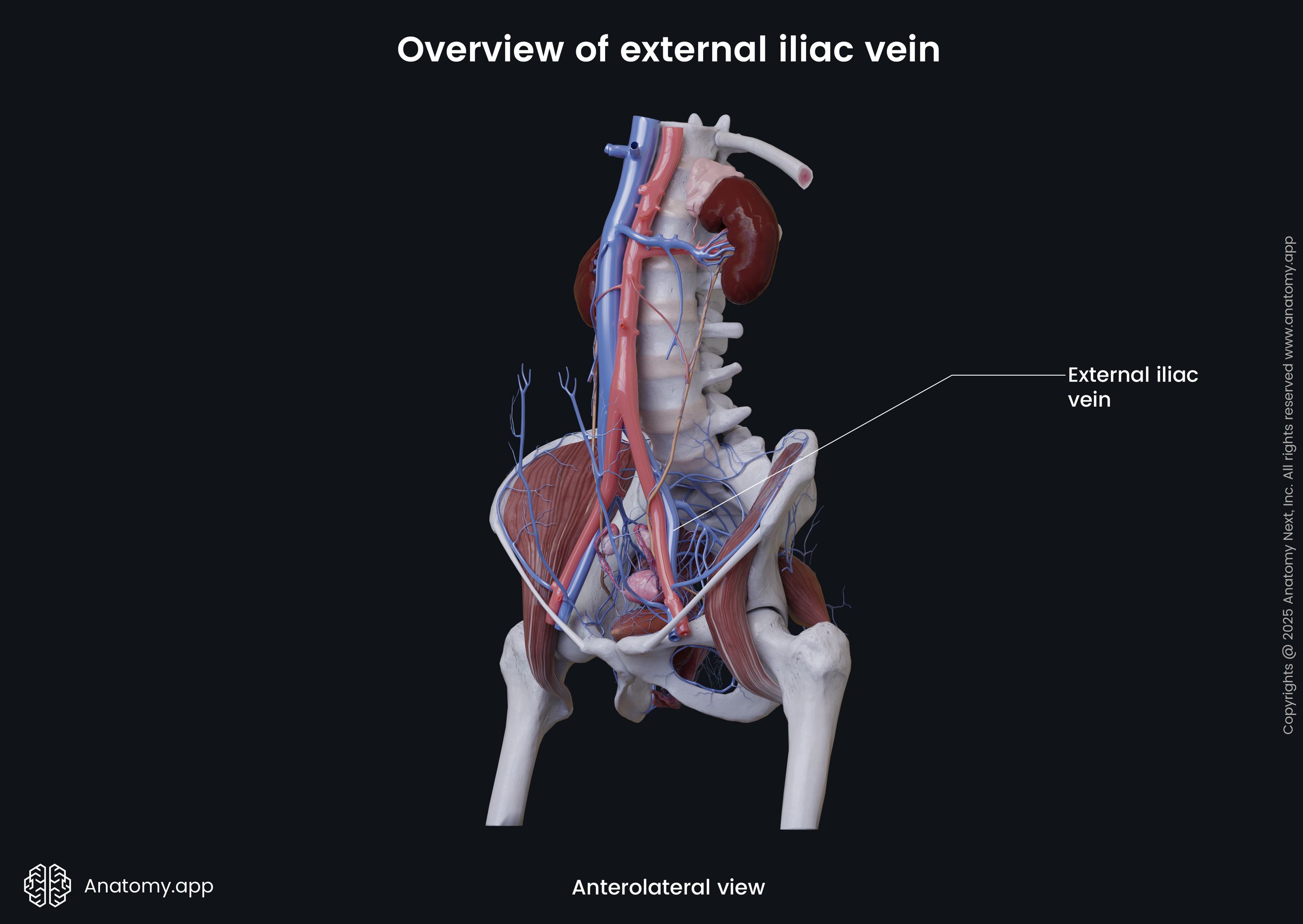
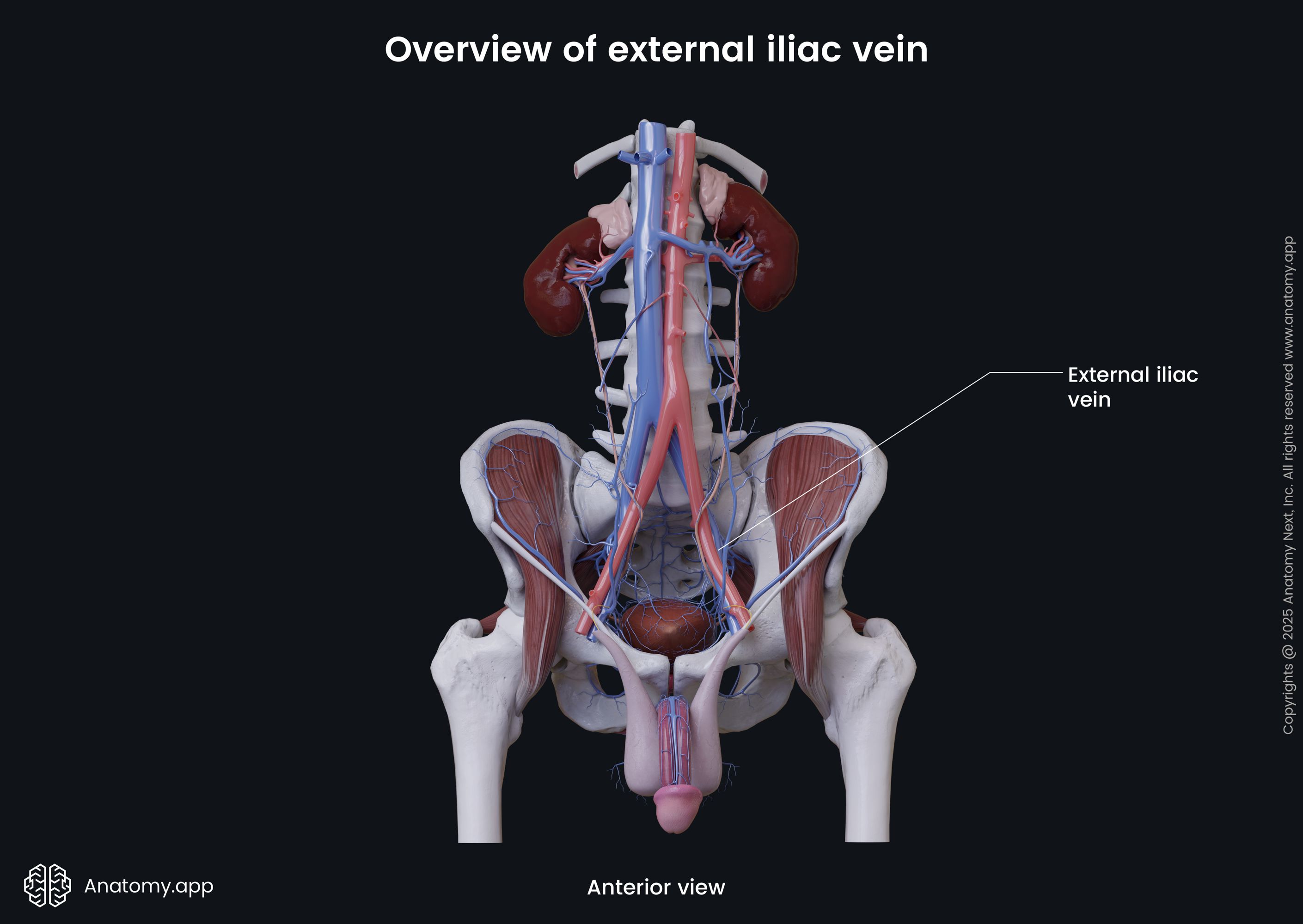
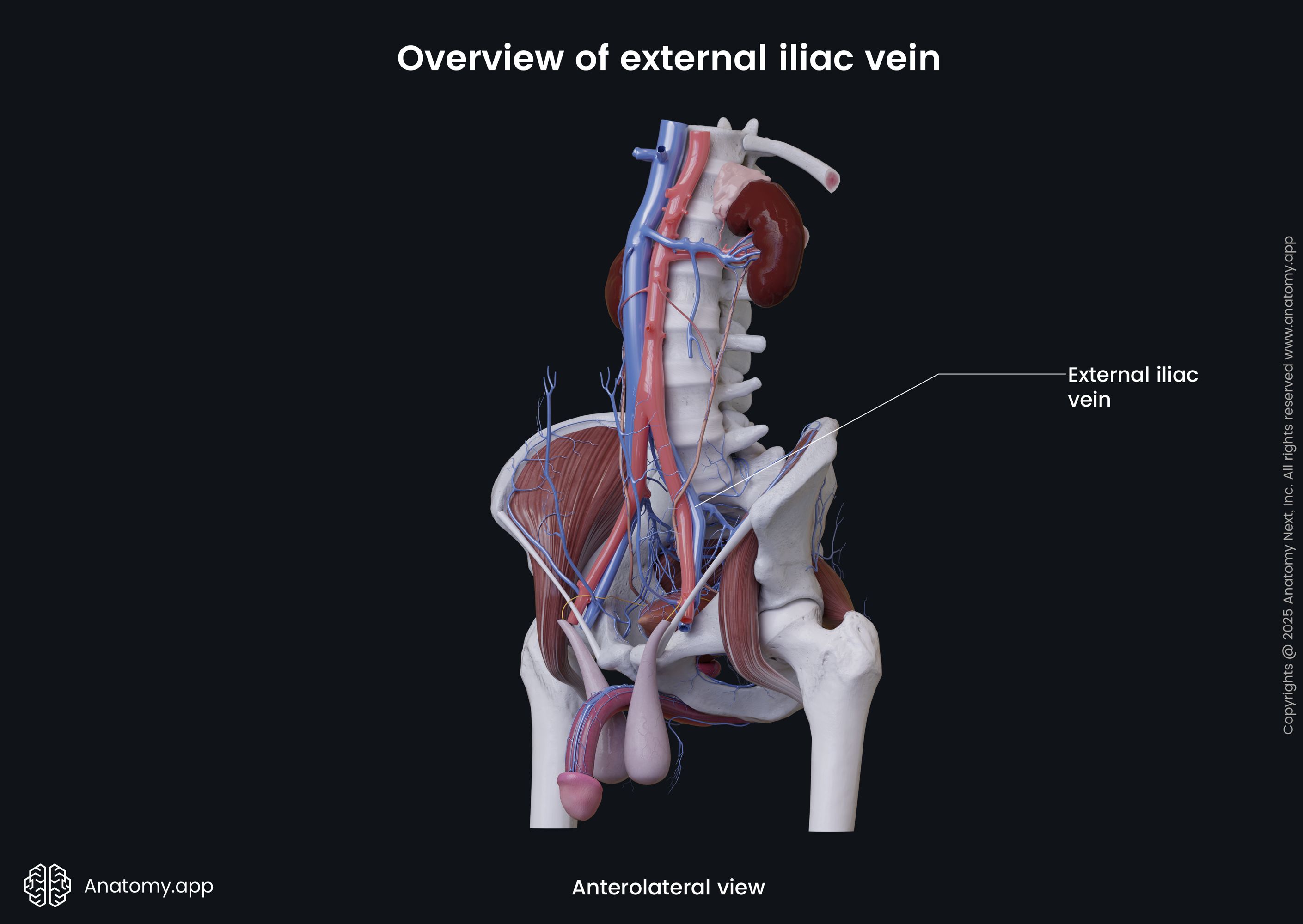
The external iliac vein begins above the inferior margin of the inguinal ligament. It enters the pelvis via the vascular lacuna and then ascends medially along the medial side of the psoas major. Reaching the sacroiliac joint, the external iliac vein unites with the internal iliac vein to form the common iliac vein.
Along its course, each external iliac vein is accompanied by the external iliac artery. On its course, the external iliac vein receives such veins as the inferior epigastric vein and the deep circumflex iliac vein.