- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Muscles of pectoral girdle
- Muscles of shoulder region
- Muscles of upper arm
- Muscles of forearm
- Muscles of hand
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
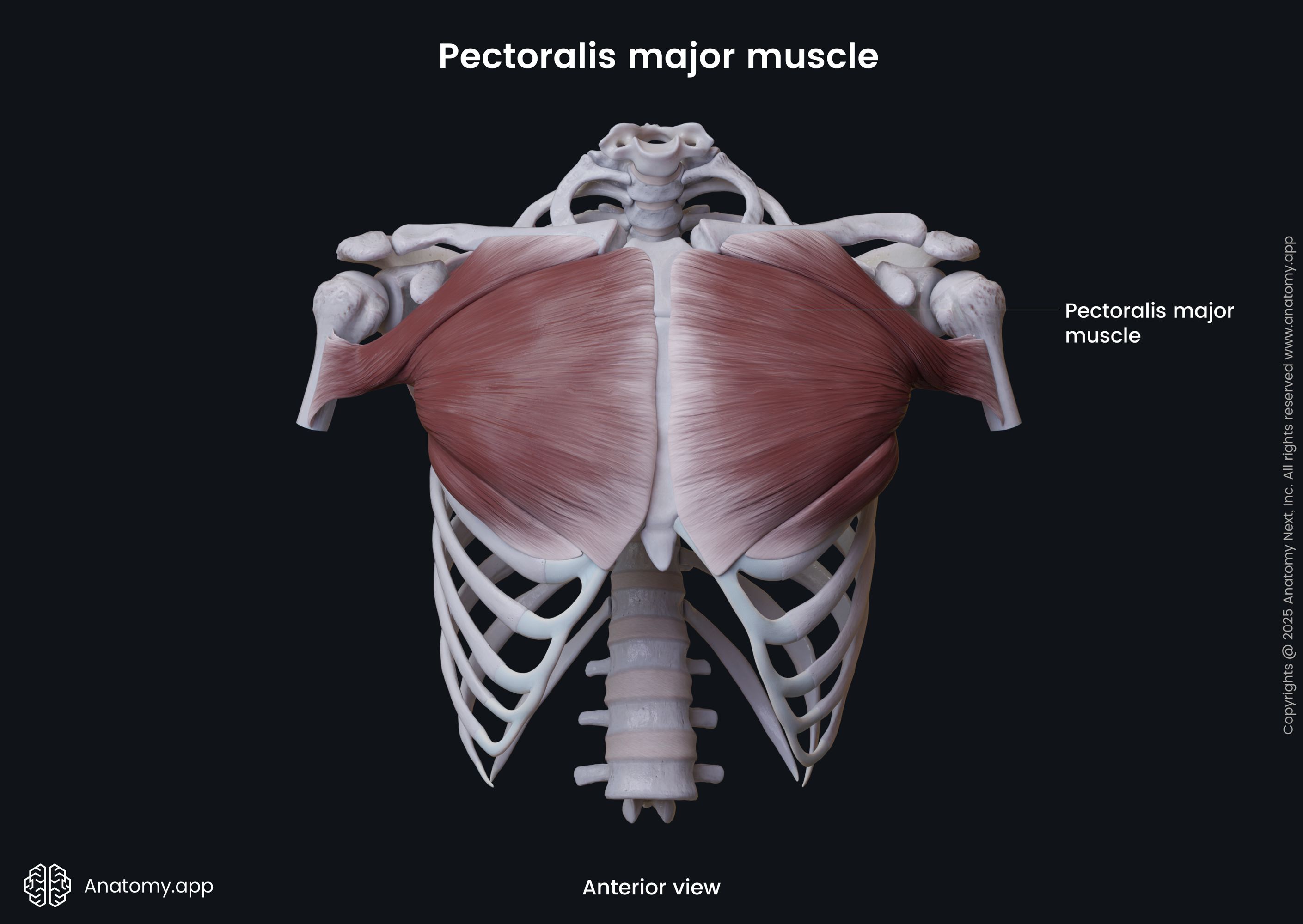
Pectoralis major
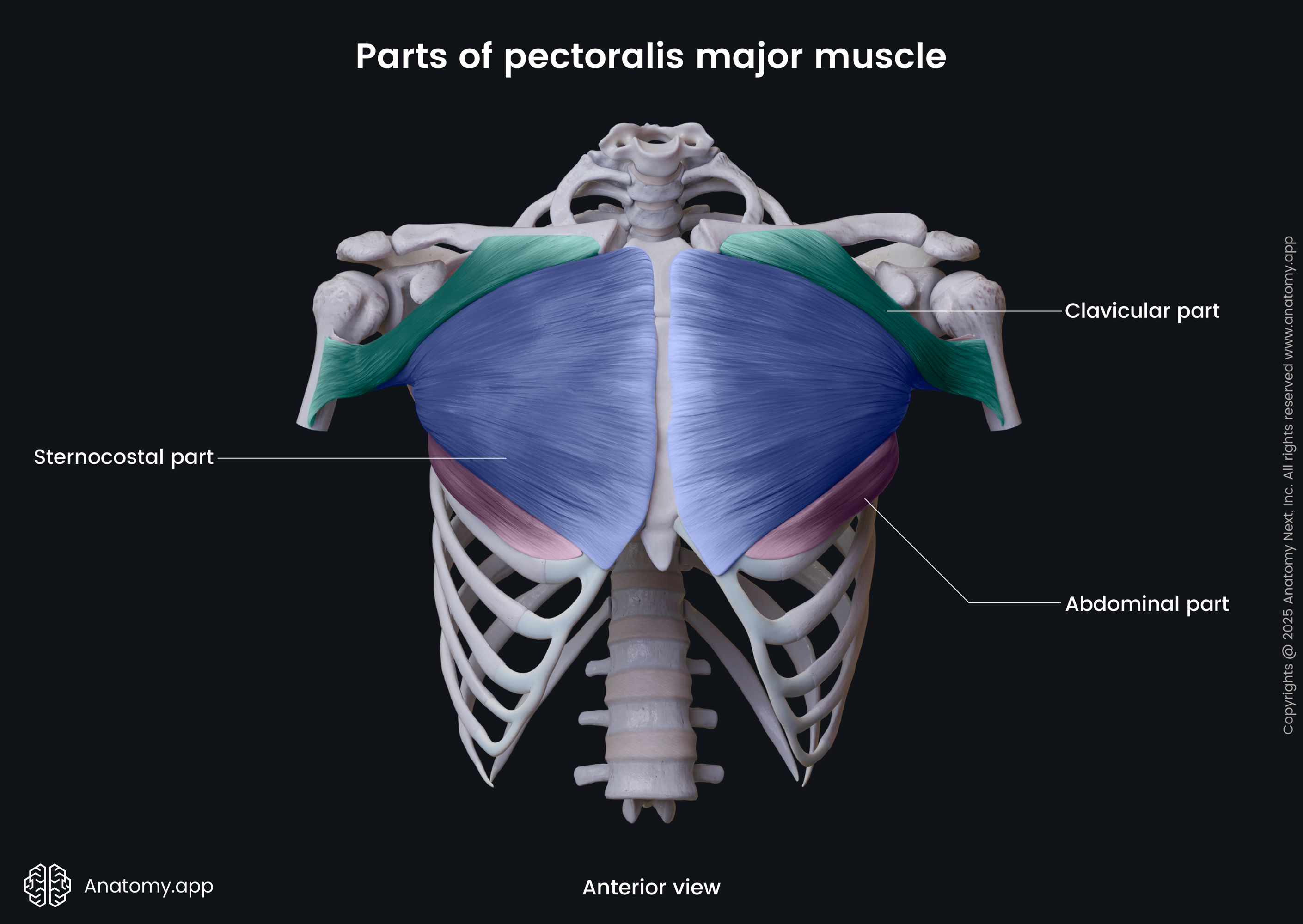
The pectoralis major (Latin: musculus pectoralis major) is a paired thick, fan-shaped thoracic wall muscle that provides movements of the upper limb. It is the most superficial muscle in the pectoral region, and it covers the anterior surface of the thorax, stretching between the shoulder and sternum. The pectoralis major has three parts - clavicular, sternocostal and abdominal. Each part has its own origin site. In the lateral direction, they all merge and share a common insertion site.
| Pectoralis major | |
| Origin | Clavicular part - anterior surface of medial half of clavicle Sternocostal part - anterior surface of sternum, upper six costal cartilages Abdominal part - anterior layer of rectus abdominis muscle sheath |
| Insertion | Crest of greater tubercle of humerus |
| Action | All parts - adduction, medial (internal) rotation of arm Clavicular part - arm flexion Sternocostal part - arm extension |
| Innervation | Lateral and medial pectoral nerves |
| Blood supply | Branches of thoracoacromial and internal thoracic arteries |
Origin
The clavicular part of the pectoralis major muscle originates from the anterior surface of the medial half (sternal end) of the clavicle. The sternocostal part originates from the anterior surface of the sternum, as well as from the upper six costal cartilages. The abdominal part originates from the anterior layer of the rectus abdominis muscle sheath.
Insertion
As written above, all three parts merge and insert on the crest of the greater tubercle of the humerus.
Action
All parts of the pectoralis major muscle provide adduction and medial (internal) rotation of the arm. The clavicular part provides flexion of the arm, while the sternocostal part is responsible for the arm extension. The pectoralis major is also one of the accessory muscles of the inspiration.
Innervation
The pectoralis major is innervated by the lateral and medial pectoral nerves - branches of the brachial plexus. The lateral pectoral nerve arises from the fifth, sixth and seventh cervical (C5 - C7) nerve roots, while the medial pectoral nerve from the eighth cervical (C8) and first thoracic (T1) nerve roots.
Blood supply
The pectoralis major muscle receives arterial blood supply from the branches of the thoracoacromial and internal thoracic arteries.