- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Superficial back muscles
- Intermediate back muscles
- Deep back muscles
- Superficial layer
- Intermediate layer (Erector Spinae)
- Deep layer (Transversospinales)
- Deepest layer
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Intertransversarii
The intertransversarii muscles (Latin: musculi intertransversarii) are small and short deep back muscles that stretch between the transverse processes of the adjacent vertebrae. Most of these muscles are located within the cervical and lumbar regions of the spine, known as the cervical and lumbar intertransversarii muscles. However, small muscular slips are also present in the lower thoracic region. Together with the interspinales and levatores costarum, the intertransversarii form the deepest layer of the deep back muscles.
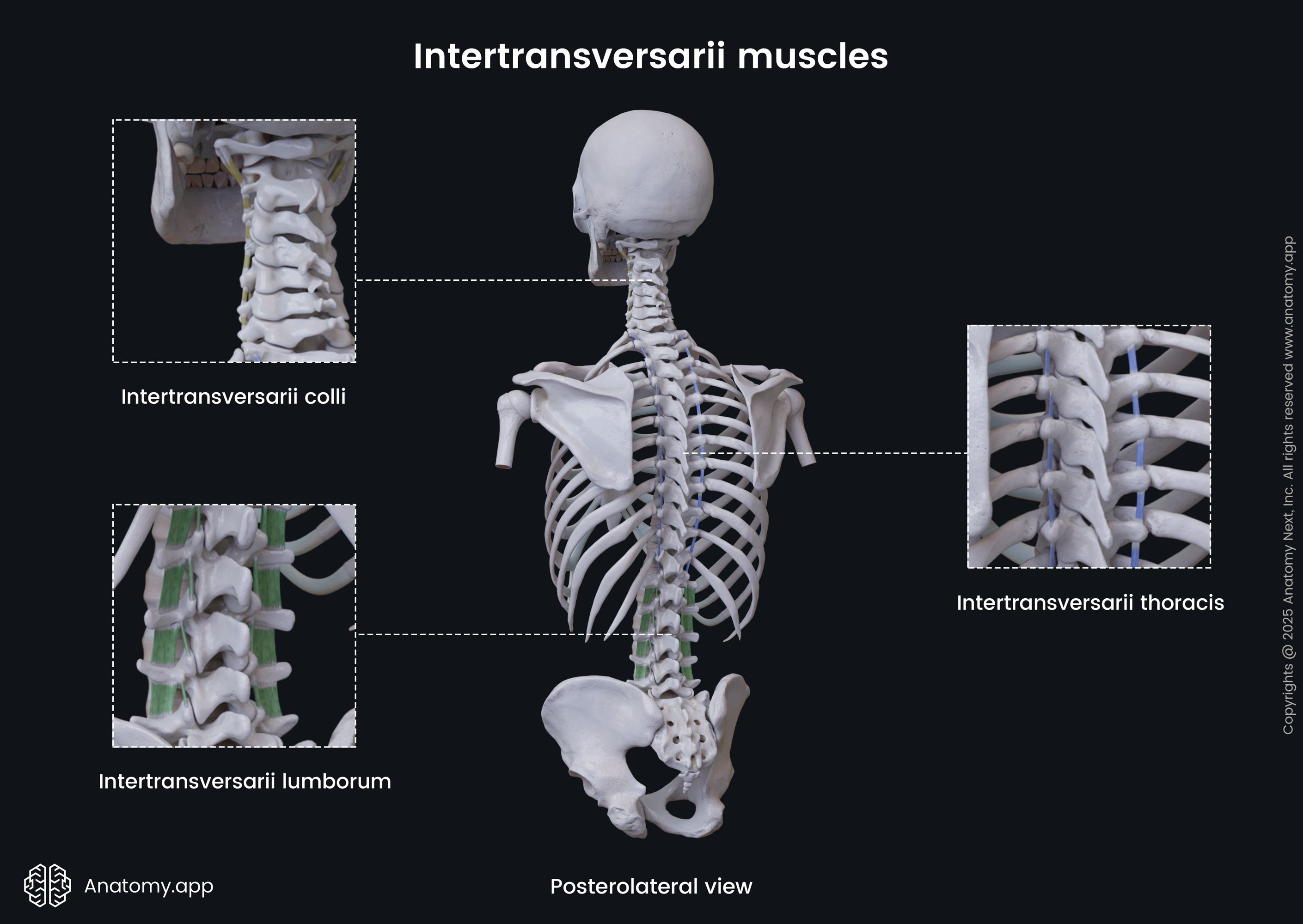
Intertransversarii colli
The intertransversarii colli (Latin: musculi intertransversarii cervicis, musculi intertransversarii colli) are located in the cervical spine. These muscles are better developed than the lumbar intertransversarii muscles. The cervical intertransversarii include seven pairs of anterior and posterior cervical intertransversarii muscles that stretch along the sides of the cervical spine.
| Cervical intertransversarii | |
|---|---|
| Origin | Anterior cervical intertransversarii - anterior tubercles of transverse processes of cervical vertebrae Posterior cervical intertransversarii - superior borders of transverse processes of cervical vertebrae |
| Insertion | Anterior cervical intertransversarii - anterior tubercles of transverse processes of adjacent cervical vertebrae Posterior cervical intertransversarii - inferior borders of transverse processes of adjacent cervical vertebrae above |
| Action | Lateral flexion of cervical spine, stabilization of cervical spine |
| Innervation | Anterior cervical intertransversarii - ventral rami of cervical spinal nerves Posterior cervical intertransversarii - ventral and dorsal rami of cervical spinal nerves |
| Blood supply | Vertebral, deep cervical and occipital arteries |
Origin
Each anterior cervical intertransversarii muscle originates from the anterior tubercle of the transverse process of the cervical vertebra. Each posterior cervical intertransversarii muscle originates from the superior border of the transverse process of the cervical vertebra.
Insertion
Each anterior cervical intertransversarii muscle inserts on the anterior tubercle of the adjacent cervical vertebra, while each posterior cervical intertransversarii muscle inserts on the inferior border of the transverse process of the adjacent cervical vertebra above.
Action
The anterior and posterior cervical intertransversarii muscles aid in lateral flexion of the cervical spine. Also, they stabilize the cervical spine.
Innervation
The anterior cervical intertransversarii muscles are innervated by the ventral rami of the cervical spinal nerves, while the posterior cervical intertransversarii are supplied by the ventral and dorsal rami of the cervical spinal nerves.
Blood supply
The arterial blood supply to the anterior cervical intertransversarii muscles is provided by the occipital, deep cervical and vertebral arteries. The occipital artery arises from the external carotid artery, the deep cervical artery originates from the costocervical trunk, while the vertebral artery is a branch of the subclavian artery. The posterior cervical intertransversarii muscles are supplied by the ascending cervical artery of the thyrocervical trunk.
Lumbar intertransversarii
The lumbar intertransversarii (Latin: musculi intertransversarii lumborum) are composed of four pairs of muscles located on either side of the lumbar spine. They extend between the transverse processes of two adjacent lumbar vertebrae. Each pair consists of a medial and lateral component, namely, the medial and lateral lumbar intertransversarii muscles.
| Lumbar intertransversarii | |
|---|---|
| Origin | Medial lumbar intertransversarii - accessory processes of L1 - L4 vertebrae Lateral lumbar intertransversarii - transverse and accessory processes of L1 - L4 vertebrae |
| Insertion | Medial lumbar intertransversarii - mammillary processes of adjacent lumbar vertebrae Lateral lumbar intertransversarii - transverse processes of adjacent lumbar vertebrae |
| Action | Lateral flexion of lumbar spine, stabilization of lumbar spine |
| Innervation | Ventral rami of lumbar spinal nerves |
| Blood supply | Branches of lumbar arteries |
Origin
The lateral lumbar intertransversarii muscles originate from the transverse and accessory processes of the first to fourth lumbar vertebrae (L1 - L4). The medial lumbar intertransversarii muscles arise from the accessory processes of the first four lumbar vertebrae (L1 - L4).
Insertion
The muscle fibers of the lateral lumbar intertransversarii insert on the transverse processes of the adjacent lumbar vertebrae. The medial lumbar intertransversarii muscles insert on the mammillary processes of the adjacent lumbar vertebrae.
Action
The lumbar intertransversarii muscles aid in lateral flexion of the lumbar spine. Also, these muscles stabilize the lumbar spine.
Innervation
The lumbar intertransversarii muscles are innervated by the ventral rami of the lumbar spinal nerves.
Blood supply
The lumbar intertransversarii muscles receive arterial blood supply from the dorsal branches of the lumbar arteries that arise from the abdominal aorta.