The Male G-spot (P-spot)

Do men have G-spots?
Everybody has heard about the female G-spot. But what about men? Do men have G-spots as well? The answer, unsurprisingly, is yes – the prostate. However, in contrast to the female G-spot, which may be challenging to find and with many researchers even being skeptical of its anatomical existence, there is no doubt that the prostate exists.
What is a male G-spot?
The prostate, or the male G-spot, is part of the male reproductive system. It is also known as the P-spot, the “P” referring to the prostate. Massaging or putting pressure on it reportedly brings sexual pleasure and produces a specific type of male orgasms, which are said to be different from penile-induced orgasms. The prostate-induced orgasms are described as more widespread and deeper and may be experienced as a full-body orgasm.
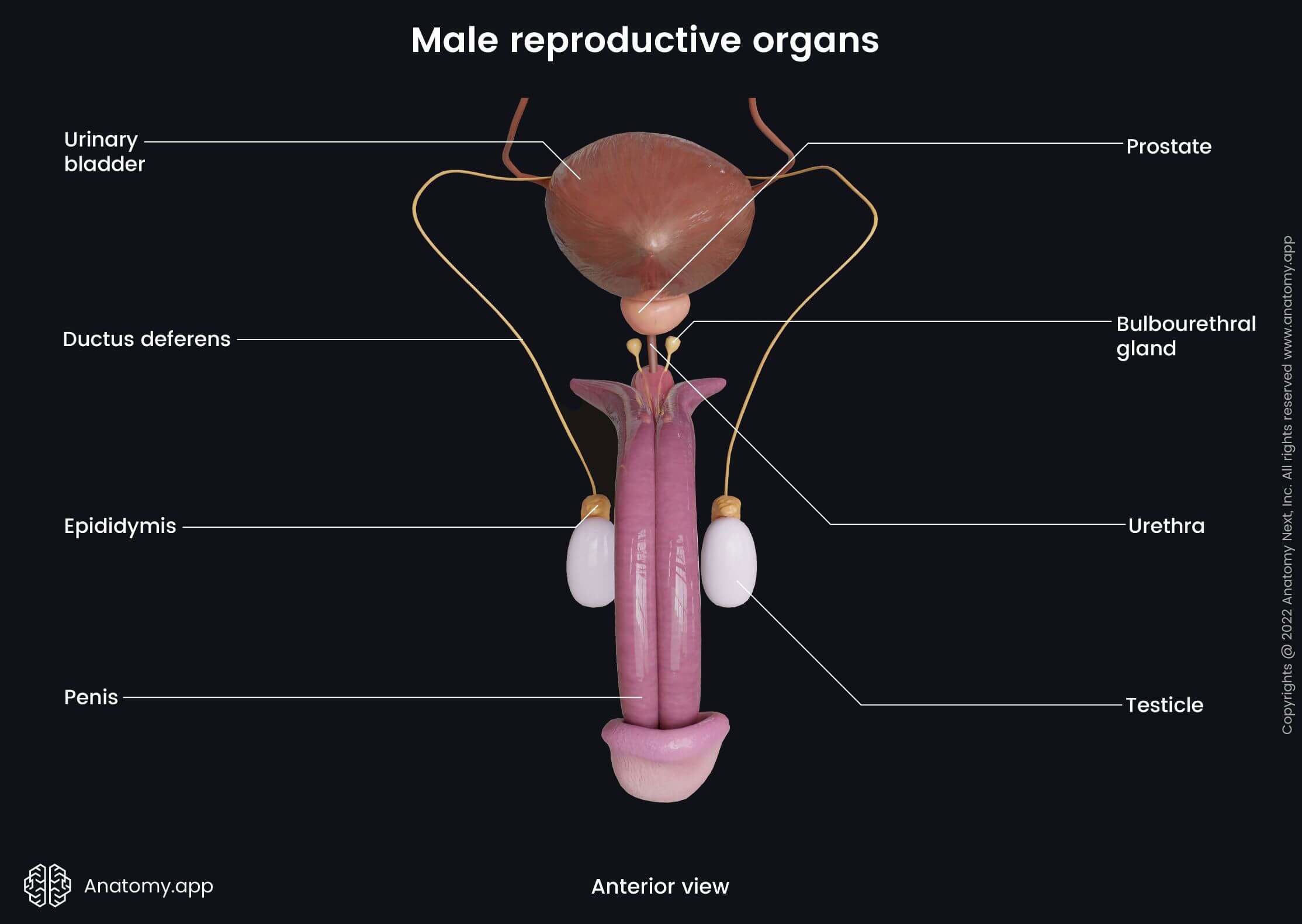
Prostate anatomy
The prostate anatomy is as follows: it’s a muscular walnut-sized gland of the male reproductive system located within the pelvis. The gland is tightly attached to the neck of the urinary bladder and surrounds the proximal part of the urethra. The urethra arises from the bladder and passes through the prostate.
The gland has a dense consistency, and its average size is 3 x 4 x 2 cm, with a weight of around 20 to 40 grams. However, the size of the prostate depends on a person’s age – it is fully developed in the late teens and usually becomes larger in older individuals.
The prostate consists of several types of tissue: smooth muscles, glandular epithelium, and connective tissue. Glandular tissue comprises the majority of the prostatic tissue, while fibromuscular tissue (muscles and connective tissue) surrounds the glands.
Functions of the prostate
The prostate has multiple functions, but its primary one is to produce a milky fluid that nourishes, protects and transports sperm. The prostate is an exocrine gland – its produced fluid is secreted to a body surface through ducts.
During ejaculation, the prostate releases prostatic secretions into the urethra via small excretory ducts. In the urethra, the prostatic secretions mix with the sperm and fluid produced by the seminal vesicles to create the semen. And finally, the semen is then ejaculated out of the male body.
The prostatic secretions are slightly alkaline, high in protein content, and they protect and nourish the sperm. More precisely, they increase the activity and chance of survival of the spermatozoa.
Another function of the prostate is to act as a sphincter that limits the flow of urine during ejaculation. The prostate also contains a small amount of endocrine cells, which in contrast to exocrine cells release substances (hormones) into the bloodstream.
Finally, the prostate is highly sensitive to touch. Its stimulation invokes pleasurable sensations and can develop into a full-body orgasm. Therefore, the prostate is believed to have both procreative functions because of its involvement in reproductive aspects of male ejaculate, and recreative functions, as it plays a role in sexual pleasure.
Where is the male G-spot?
It is well known where the male G-spot is located: the prostate is an internal organ situated within the lesser (true) pelvis. It’s located behind the pubic symphysis, below the neck of the urinary bladder, and between the base of the penis and rectum. While there are heated debates about the exact location of the female G-spot, the location of the prostate is well known.
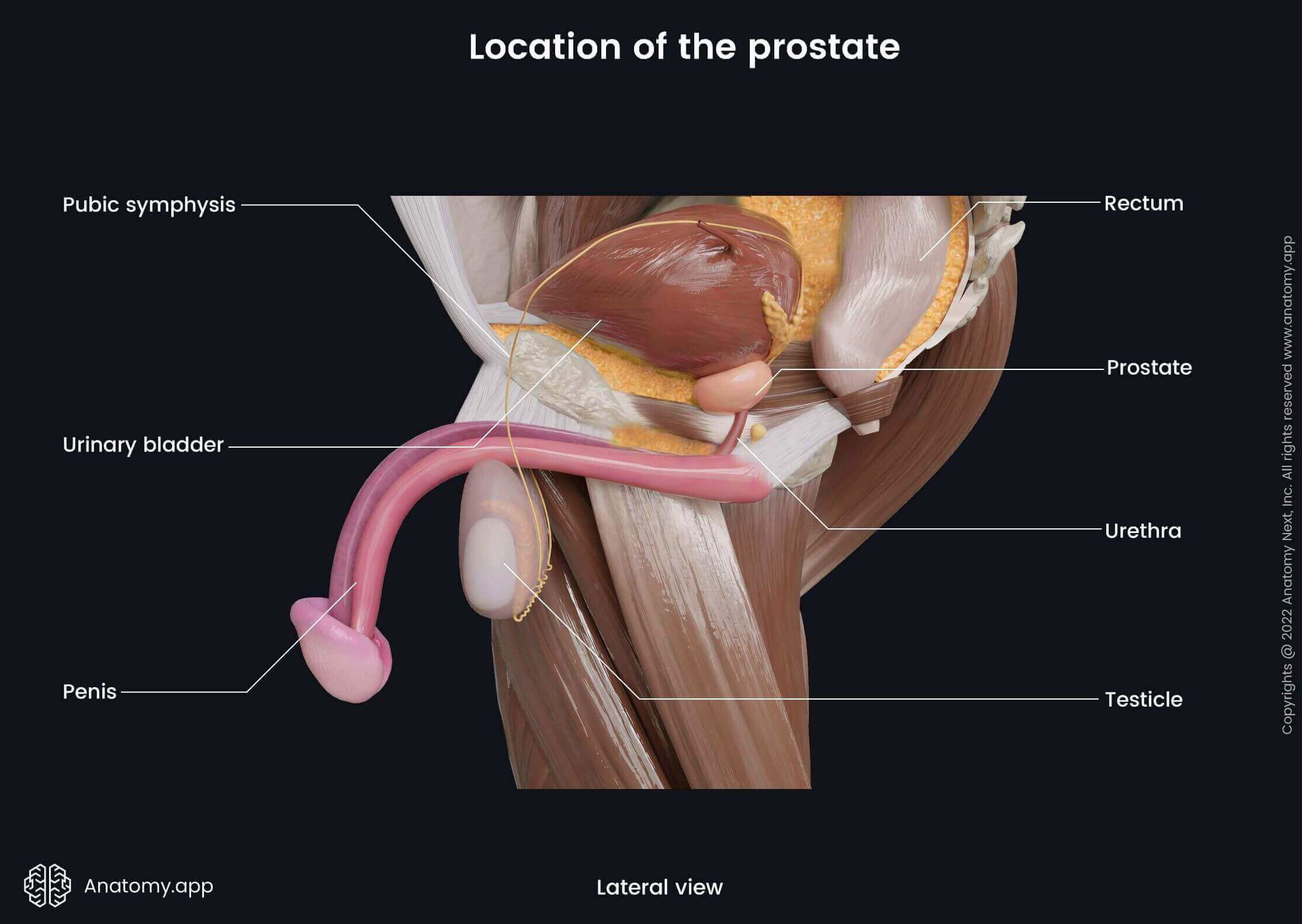
How to find the male G-spot?
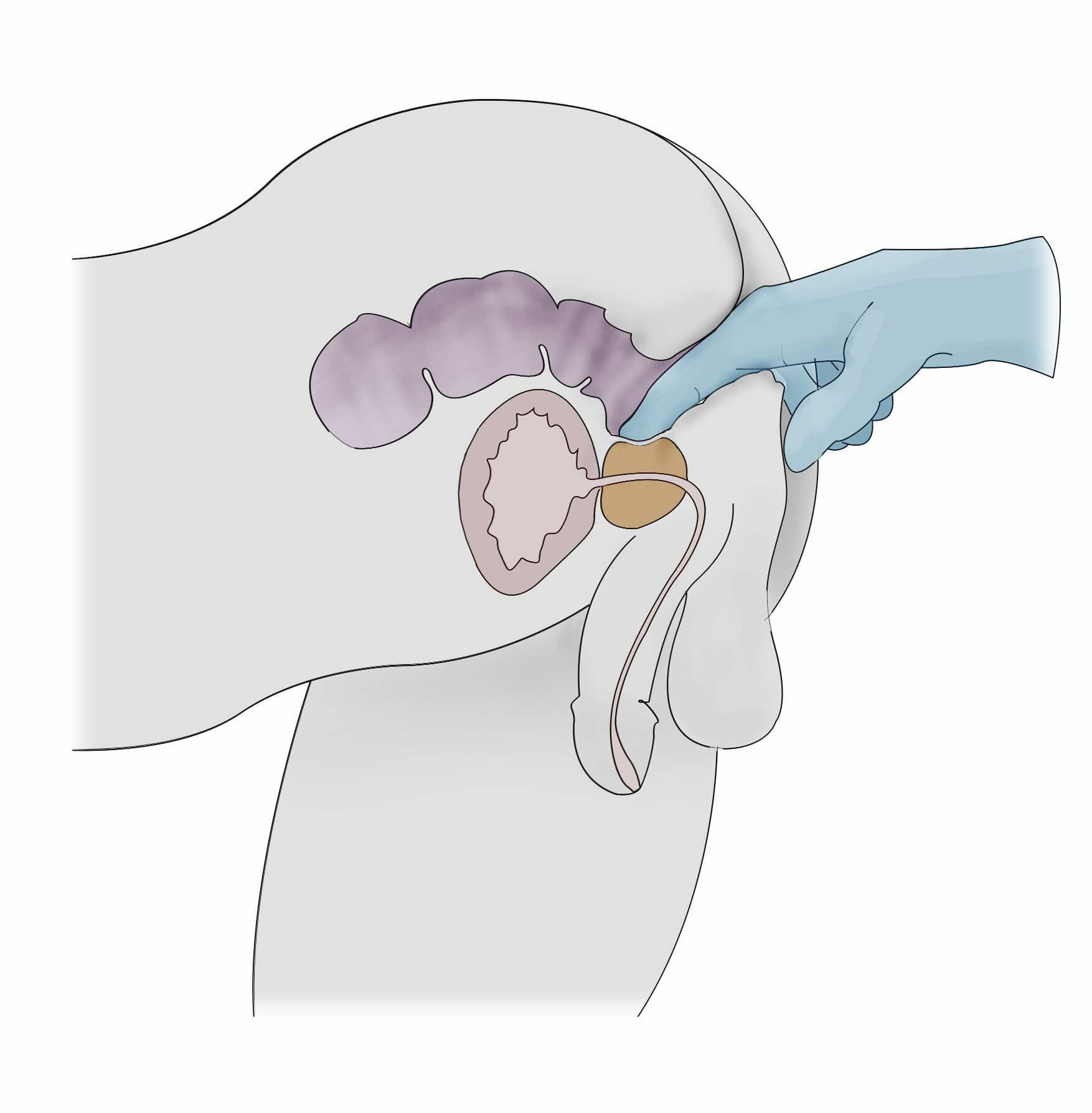
It’s quite easy to find the male G-spot – during a standard prostate examination, the prostate is usually detected by inserting a lubricated finger in the anus, going approximately 2 inches (5 centimeters) inside the rectum, and pressing the finger towards the belly in an upward direction. The prostate feels like a rounded lump in the rectal wall. It is then palpated to identify its size, consistency and other criteria.
As far as pleasure is concerned, the prostate may be stimulated both internally through the rectum and also externally – by touching the area between the scrotum and the anus. This area is known as the perineum. There won’t be any bumps to feel, but it is reported that putting pressure on this body part may lead to prostate-induced sexual pleasure.
Science behind male G-spot pleasure
There is currently not much scientific evidence to describe precise mechanisms behind male G-spot pleasure and prostate-induced orgasms.
In 2017, a scientific review was published in Clinical Anatomy that sums up numerous reports in the medical literature about prostate anatomy, functions, and involvement in eliciting sexual responses. According to this review, there are two possible ways in which a prostate massage may activate pleasurable experiences and orgasms.
One theory is that a network of nerves that is attached to the prostate, penis, and urethra is responsible for the male prostate orgasm. It is called the prostatic plexus. According to this theory, nerves of this plexus receive stimuli from massaging or putting pressure on the prostate and convey information to the brain, thus creating an experience of sexual arousal and pleasure.
Another theory, also described in the mentioned review, claims that it may all start in the mind, meaning that the pleasurable experience during prostate stimulation may be first created (or intensified) in the brain and from there influencing the sexual responses in the body. The study suggests that by focusing attention on the prostate during its massaging, in time, it is possible to reach more satisfaction with each following massage.
Male erogenous zones: what are the others?
In order to enrich sexual experiences, men and their partners might also be interested in getting to know other male erogenous zones. Of course, the penis is the most obvious part of the male body that produces sexual pleasure; however, there are others too.
A 2013 study about erotic sensations in different body parts that surveyed around 800 men and women concluded that the most sensitive erogenous zones reported by men were the penis, followed by the mouth and lips, scrotum, inner thigh, and the back of the neck.
However, research suggests that actually, all body parts may respond to touch and provoke sexual arousal. In a study published in Archives of Sexual Behavior, 704 participants (male and female) were shown body images of the same and opposite sex. They were asked to color areas that they themselves or the members of the opposite sex would experience as sexually arousing when stimulated by touch. Both experiences, pleasuring themselves or having sexual interactions with another, were taken into account.
From the reports of the participants, the researchers created a body map of erogenous zones. They concluded that practically all body parts might elicit sexual arousal from touch. Of course, that depends on countless factors, and some areas are more sensitive than others. Yet, it seems that we have more than a few erogenous zones and vast possibilities for sexual explorations, pleasuring ourselves and others.
Summary
- The male G-spot, also called the P-spot, is the prostate. Stimulating the prostate may bring pleasure and lead to a full-body orgasm.
- The prostate is an internal reproductive organ. It is a walnut-sized gland that consists of smooth muscles, glandular epithelium, and connective tissue.
- It is an exocrine gland that produces secretions that mix with sperm. It not only demonstrates procreative functions, as it is involved in protecting and nourishing the spermatozoa, but it also has recreative functions, as it participates in sexual responses.
- The prostate is located in front of the rectum and behind the base of the penis. It can be found about 2 inches (5 cm) inside the rectum and can be felt like a rounded bump in the frontal rectal wall.
- Mechanisms behind prostate-induced pleasure and orgasm are not clear. However, there are theories of two main ways how the male G-spot pleasure develops: through the stimulation of a nervous plexus attached to the prostate and through a neural pathway beginning in the brain.
- As reported by men and their sexual partners, practically all body parts may bring sexual arousal. However, the most sensitive areas of the male body are the penis, mouth and lips, inner thigh and scrotum, as well as the back of the neck.