How AI is Transforming Medicine

The growing integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in medicine has sparked curiosity about the truth behind this innovative technology.
Did you know that an AI system can analyze thousands of data points in just a few seconds, a task that might take a human expert several hours, or even days, to complete? This staggering capability of Artificial Intelligence is not a futuristic fantasy – it's the current state of play in the field of medicine.
A doctor, aided by AI, can sift through vast amounts of medical data – patient histories, lab results, genetic information – in the blink of an eye. This speed and precision are revolutionizing how we approach healthcare, making it more personalized and efficient.
Want to learn more about how AI works in medicine? In this blog, you will explore the transformative impact of AI in medicine and the challenges and promises it holds for the future.
What is Artificial Intelligence in Medicine?
AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and robotics can help improve healthcare by enhancing medical services and research efficiency. They can assist healthcare professionals in providing better care and finding new solutions. They can also automate and optimize various tasks and processes in healthcare.
Training in artificial intelligence for medicine helps analyze medical data, make decisions, select treatments, reduce complications, and improve patient experiences and health outcomes. This advancement in the healthcare sector increases efficiency and access to care.

History of AI
Artificial intelligence was first introduced in medicine in the late 1950s, but several limitations prevented its widespread application in the healthcare sector. However, in 2007, a groundbreaking question-answering system was first used to analyze unstructured data to generate answers; later, this technology emerged as a powerful tool and paved the way for evidence-based medicine and clinical decision-making.

The projections estimate significant growth of AI in the future. According to stats, AI in healthcare is expected to reach $45.2 billion by 2026 worldwide.
Applications of AI in Medicine
AI is emerging as a game-changer in the following ways:
1. Disease detection and diagnosis
The integration of AI in medicine ensures effective detection and diagnosis of diseases. It assists healthcare professionals in analyzing patient records, predicting outcomes, interpreting medical images, and making timely interventions. Moreover, it makes the process of disease detection automated, precise, and fast.
Following are some of the applications of AI in medical diagnosis.
AI in radiology
AI algorithms are designed to analyze medical images with the precision that allows radiologists to make accurate diagnoses. In 2020, a study was conducted on an artificial intelligence system developed to identify breast cancer. The results concluded that the AI system surpasses clinical radiologists in breast cancer prediction. Another study on MRI data analysis showed that the AI algorithm accurately detects inflammatory changes in the early phases of rheumatoid arthritis.

AI in pathology
AI automates the process of analyzing histopathological images and allows for a more comprehensive analysis of tissue samples, which speeds up the diagnostic process and improves accuracy. It helps pathologists identify various tumors and other medical conditions. A study concluded that deep learning models assist pathologists in detecting cancer subtypes and predicting specific gene mutations from histopathology images.
AI in endoscopy
The detection of diseases during endoscopy has become efficient with AI technology. Researchers found that AI systems can promote the detection of colorectal polyps, gastric and esophageal cancer, and lesions in endoscopy.
A practical convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithm was developed to detect small intestine lesions in capsule endoscopy images automatically. The results showed that combining endoscopy with AI increased sensitivity and precision in localizing bowel lesions.
AI in cardiology
AI can predict cardiovascular risks precisely, ensuring timely intervention and preventative care.
AI in gastroenterology
Artificial neural networks accurately diagnose gastroesophageal reflux disease and atrophic gastritis. It can also predict outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal bleeding, inflammatory bowel disease, and metastasis in colorectal cancer.
AI in ophthalmology
AI has revolutionized vision care by providing immediate detection of retinal diseases. In 2018, a fully automated AI diagnostic system accurately detected intraretinal cystoid fluid in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration.
AI in genomics
AI algorithms aid in the interpretation of genetic information. They can efficiently identify genetic variants and mutations and use this genomic data to predict the risk of diseases. Similarly, these algorithms can predict how a certain type of cancer will progress in a patient. Furthermore, the use of deep learning technology not only facilitates researchers' understanding of the function of genes in different biological processes but also enhances the functionality of gene editing tools.
2. Personalized treatment
AI offers tailored treatment solutions to patients based on their medical history, genetic information, treatment responses, lifestyle, and preferences, significantly improving patient health outcomes.

Personalized medicine with AI empowers both patients and healthcare practitioners. AI-powered tools analyze data, develop trends, and provide physicians with valuable insights that help design precise treatment plans. Similarly, these tools constantly monitor patient health and provide real-time feedback, increasing their engagement and giving them more control over their healthcare.
3. AI in surgery
One of the remarkable applications of AI in medicine is the surgical AI system, which allows surgeons to perform remote operations using robotic systems. These systems can enhance the convenience and accuracy of surgery by reducing human errors. A surgical AI system that the FDA has approved for clinical surgery is the da Vinci surgical system. (The FDA is a key agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services that ensures the safety and effectiveness of medical devices).
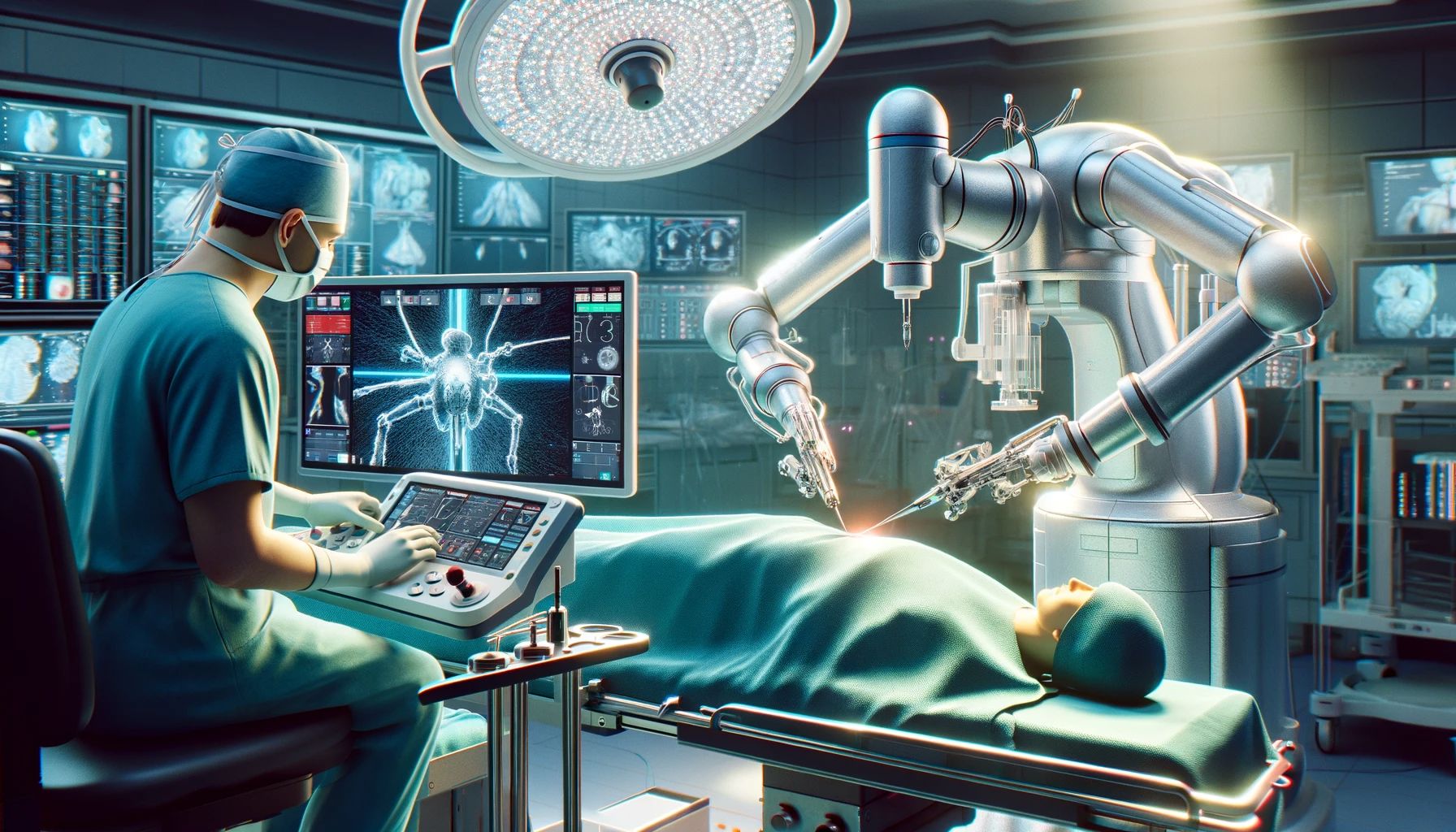
The da Vinci surgical system has three parts - a console for the surgeon, a system for manipulating the robotic arms, and a system for imaging. The console lets the surgeon control the robotic arms, which can do accurate movements and actions.
The imaging system provides high-definition 3D images of the surgical site, which can improve the surgeon's visibility and orientation. The da Vinci surgical system has revolutionized surgery by enabling minimally invasive procedures that can reduce blood loss, pain, scarring, and recovery time. A review concluded that thyroid surgery through the da Vinci system offers excellent postoperative cosmesis and voice outcomes.
4. Drug discovery and development
AI has revolutionized the pharmaceutical industry by accelerating and optimizing the drug discovery process. It reduces human workload and produces quality drugs with high efficacy and fewer side effects.
AI tools help researchers analyze complex datasets, identify potential compounds, predict target sites, and design drugs. These tools can predict drug interactions that help in optimizing multi-drug treatment regimens.
Moreover, AI technologies can easily predict the biomarkers associated with specific diseases, which allows us to select the patient population for clinical trials. It also provides more personalized treatments, leading to patient satisfaction.

An artificial intelligence-driven drug discovery company, Insilico Medicine, conducted a phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetics clinical trial of INS018_055, a potential first-in-class drug for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). The trial announced encouraging top-line results of this drug for IPF.
5. AI for medical students
AI also makes medical studies easier, more accessible, and more enjoyable. It provides personalized and interactive learning resources that suit student needs and goals.

It helps better understand and remember clinical diseases and practice diagnostic skills in a safe and realistic manner. It can also assist in organizing study materials and assignments, finding and using global resources, and receiving feedback on a student's progress. However, AI is still evolving and combining human input with AI assistance is the best way to learn medicine.
Anatomy.app is an excellent example of how AI features can be combined with human-generated content. Currently, the 3D Anatomy section of Anatomy.app combines human-generated 3D materials and textual information with text-to-speech AI features. This feature allows students to explore the human body in a realistic 3D view while listening to the textual description as they explore the particular 3D model.
Advantages of AI in Medicine
The transformative advantages of AI include:
- Improved efficiency and minimized errors
AI is making healthcare better by improving accuracy, efficiency, and decision-making. It helps healthcare staff by doing boring administrative jobs, like keeping track of patient records, analyzing data, and booking appointments. This makes their work easier and reduces the chance of mistakes. It also makes the workflow smoother by facilitating better communication and integration between administrative and clinical processes.
AI-powered systems can efficiently store medical records, analyze vast amounts of data, and develop trends to provide valuable insights to physicians, thereby improving their decision-making.
- Improved patient care
AI can help patients take more control over their healthcare journey by giving them easy access to medical information and guidance. Patients can use AI platforms to learn about their medical conditions and the available treatment options. They can also choose how they want to receive the information, whether by reading or listening.
AI-powered wearable devices monitor patients’ health metrics in real-time and generate personalized insights. They quickly identify and detect potential health issues and give tailored recommendations for preventative care according to the patient's conditions and preferences. With the help of data analytics, physicians can design personalized treatment plans for better patient outcomes. A systematic literature review concluded that AI-enabled decision support tools significantly enhance patient health outcomes by improving drug management and error reduction.
AI facilitates remote consultations and enhances communication between physicians and patients. In addition, AI-powered chatbots and virtual health assistants provide 24/7 support and guidance by answering patients’ queries and offering adequate medical advice.

- Cost efficiency
Integrating AI in medicine ensures cost effectiveness through resource optimization, automation of time-consuming tasks, early detection, predictive maintenance, and telemedicine.
Continuous health monitoring by AI systems helps physicians make timely and accurate diagnoses, which can lead to long-term cost savings. This enhanced diagnostic accuracy assists physicians in planning preventative care, which eliminates the need for unnecessary treatments and hospital administrations. Similarly, digital consultations save time and resources, minimize associated expenses, and make healthcare more accessible. When healthcare becomes affordable and easy to access, it ultimately improves healthcare outcomes and quality of life.
- Efficient healthcare delivery
The implementation of AI-powered tools enhances the overall efficiency of healthcare processes.
AI systems continuously update patients' records and analyze data, which reduces operational burdens and provides physicians with the most recent information. Similarly, real-time data analytics minimizes waiting times and enables healthcare professionals to provide immediate patient care.
AI aids in interpreting diagnostic tests and medical imaging, making it easier for physicians to diagnose. It generates evidence-based recommendations for treatment options and care plans for each patient.
Disadvantages of AI in Medicine
Despite the promising advantages of AI in healthcare, there are certain limitations that hinder its acceptance. Some of the common disadvantages of AI are as follows:
- Data privacy and security concerns
With the adoption of AI technologies to manage patient-sensitive information, the risk of data privacy becomes a prominent concern. This is because AI systems are highly susceptible to security risks and unauthorized access, leading to compromising patient confidentiality.

In addition, cybercrimes are becoming more sophisticated, which seriously threatens the integrity of medical records and the functioning of medical services.
- Risk of over-reliance on AI
Over-reliance on AI algorithms is another threat in healthcare that can result in inappropriate treatments, missed diagnoses, and harmful patient outcomes. It can critically reduce the involvement of physicians in decision-making processes.
Furthermore, AI lacks emotional intelligence, making it difficult to provide quality care to patients with emotional connections.
- Ethical dilemmas in AI decision-making
The lack of accountability and transparency in AI-driven healthcare makes it challenging to understand how decisions are made. So, when physicians rely solely on AI-driven choices, it may result in biased or discriminatory outcomes that directly impact patient care. It can also generate mistrust among patients and healthcare physicians.
The lack of transparency in how AI algorithms make decisions is a significant problem in healthcare. It generates mistrust among patients and physicians and raises questions about how specific conclusions are made.
Moreover, the absence of guidelines regarding AI's safe and effective use in healthcare makes it difficult to navigate its ethical use.
Challenges Associated with the Implementation of AI
The application of AI poses various challenges, including:
- Compromised data quality
Inaccuracy and inconsistency of data across various platforms due to a lack of standardization can significantly impact the performance of AI algorithms.
AI tools analyze the stored medical data to develop trends and generate insights. Any incomplete or missing data in a patient's medical history can lead to inaccurate diagnoses and errors in treatment recommendations.

- Physician and staff training
Having an adequate skill set to understand AI is another challenge. AI is designed with complex algorithms and interfaces, which require comprehensive and ongoing training to harness its full potential for patient care.
Healthcare staff usually have demanding schedules, which makes it challenging to manage time for comprehensive training on AI applications. In addition, some professionals might be less comfortable switching to digital systems.
- Integration into existing healthcare systems
Successful integration of AI in existing healthcare systems requires careful planning to avoid disruption in the workflow of healthcare setups. Most healthcare facilities lack systems that can seamlessly accommodate advanced AI technologies.
Establishing the necessary infrastructure for AI requires considerable investment, which might be a constraint for some organizations.
Possible Solutions
To overcome the dangers of AI in medicine, we must opt for a multifaceted approach:
- Strategies for improving the quality of data
Data quality is crucial for reliable healthcare outcomes, so you must develop and implement strategies to eliminate data inaccuracy. For instance, conduct regular data management audits, implement robust data collection processes, maintain data in the correct format, and set data metrics for standardized data.
These strategies help minimize errors and enhance data consistency, which aids in making precise diagnoses, increases physician-patient trust, and enhances the effectiveness of AI applications.
- Ensuring patient safety and privacy
Comply with HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability) privacy and security to keep patients' data safe and secure. Invest in privacy-enhancing technologies to safeguard data from unauthorized access and avoid security breaches. It is also important to clearly communicate and collaborate with regulatory bodies to align practices that meet the highest privacy standards, prioritizing patient safety.
- Ethical use of AI
Conduct rigorous testing to identify potential biases in the AI model. Establish transparent guidelines and accountability frameworks to avoid misinformation and maintain integrity.
Healthcare professionals should be trained to evaluate AI results to critically minimize the risk of errors. In addition, make sure that AI does not replace human surveillance; instead, it should serve as a supportive tool to improve the decision-making process.
The Future of AI in Medicine
The advancements in AI technology will make an even more powerful impact in the healthcare sector. For instance, AI systems will become more regulated, which will enhance their credibility, and they will be given more responsibility.
It will improve patient management by efficiently extracting crucial patient information, streamlining the process of preparing consultation summaries, recommending interventions proactively, and providing more personalized treatments based on patients' histories. It will also improve diagnostic processes by introducing specialized diagnostic expertise into primary care.

Such sophisticated AI tools will not replace human physicians but augment their efforts for better patient care.
Conclusion
AI holds the potential to change the whole landscape of the health sector and medical research. It focuses on providing a patient-centered, efficient, and adaptable healthcare system.
The remarkable AI technology increases efficiency in disease detection, personalized treatment, remote monitoring, and preventative care, leading to better health outcomes. It also aids in streamlining administrative tasks, drug discovery, clinical trials, and medical education, which saves time and optimizes resource allocation.
Commonly Asked Questions
Is AI used in medicine?
Yes, artificial intelligence is integrated into various medical processes to improve health outcomes and patient experiences.
How can AI be used in medicine?
AI is used in medicine for disease detection, personalized treatment planning, drug discovery, clinical decision support, medical imaging analysis, health monitoring, and patient care management. It also streamlines administrative tasks in the healthcare sector and improves the learning experience through online courses and interactive simulations.
Where is AI used in medicine?
AI finds its application in various medical disciplines, including medical imaging, pathology, cardiology, dermatology, gastrology, neurology, cancer diagnosis, pulmonology, urology, ophthalmology, and diagnosis of rare diseases.
Who uses AI in healthcare?
AI in healthcare is used by healthcare professionals, patients, researchers, and healthcare organizations to increase convenience, efficiency, accuracy, and healthcare quality.
Why do we need AI in healthcare?
AI in healthcare offers transformative benefits such as accurate clinical decisions, improved efficiencies, early detection of diseases, reduced cost, better patient care, round-the-clock digital assistance, and much more.
Will AI replace medicine?
Artificial intelligence will not replace medicine. However, it will revolutionize various aspects of medicine by enhancing diagnostics, automating workflows, and providing personalized care to patients.