Digital Cadavers and Virtual Labs: a Futuristic Approach to Anatomy Learning

Imagine learning about the intricacies of the human body through virtual labs and digital cadavers. Sounds like sci-fi, isn't it? But it's real, and it's happening now.
Gone are the days of thick textbooks and lab cadavers. We're entering an era of digital anatomy tools. These tools are not gimmicks - they're changing anatomy in unimaginable ways.
Today, we will clue up our readers on virtual and remote anatomy education. So, let's start and see what this new era has for us!
Understanding the Concept of Digital Cadavers and Virtual Labs

Digital cadavers are computer-generated models of human dead bodies created for educational and medical purposes. They are made by scanning real cadavers with high-resolution imaging techniques, such as CT, MRI, or cryosectioning.
Alternatively, 3D artists can process radiological materials in collaboration with medical doctors to create highly detailed models of anatomical structures, such as bones, muscles, organs, vessels, and nerves. These flexible models provide 3D visuals of anatomical structures and allow the users to view the body from different angles for better understanding. They effectively simulate physiological processes and pathologies, which ensures an enhanced learning experience. You can access these 3D visuals and materials online through various apps, one of which is mentioned later in the article.
On the other hand, virtual labs are online platforms that simulate the anatomy lab experience. It provides a digital space for researchers and students to perform experiments and tests on digital specimens. The idea of a virtual lab is becoming increasingly popular because of its online accessibility, enhanced interactivity, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
The Origin of Digital Cadavers and Virtual Labs
In the 15th and 16th centuries, Leonardo da Vinci and Andreas Vesalius came forward with the most sophisticated anatomical illustrations that reshaped anatomical knowledge and medical science. Their groundbreaking work became the analog ancestor of the virtual reality cadavers we use today.
After years of hard work to revolutionize anatomy, the real breakthrough came in the 1990s, when the Centre for Human Simulation (CHS) created the first digital database of a complete human cadaver – Visible Human Project (VHP). Advanced techniques, including magnetic resonance imaging, computed tomography, and cryogenic slicing, were used to develop VHP. These digital human models opened up new possibilities for anatomy education and research.
Today, multiple universities rely on virtual cadavers and labs to offer students improved and practical learning experiences. These tools allow students to explore the bodily features in 3D, zoom in and out, rotate, and dissect the materials on a screen.
What Factors are Contributing to the Rise of Digital Materials and Tools in Anatomy Learning?

Anatomy education is undergoing a digital transformation as more and more educators and learners are adopting digital materials and tools to enhance their learning outcomes. This shift is driven by various factors, such as:
- The COVID-19 impact
The pandemic brought unprecedented challenges to the education sector and forced many institutions to shift to online modes of delivery. Platforms responded by providing innovative solutions that enabled online learning, such as interactive simulations, virtual labs, and 3D models. Since then, digital learning has become more prevalent and accepted in the educational world, as it offers many benefits over traditional methods. The digital materials are accessible anytime, regardless of the location or situation of the learners.
- The shortage and ethical issues of cadaver supply and disposal
The use of real human cadavers for anatomy education is declining because of challenges like accessibility and maintenance. Getting access to human cadavers is a lengthy process involving numerous legal and ethical issues. Besides, the processes associated with cadavers, like preservation, transportation, maintenance, storage, and safe disposal, significantly elevate the expenses.
On the contrary, digital cadavers and virtual labs bypass these issues and eliminate the need for physical resources. It offers personalizations and 3D visualizations, allowing students to perform the same dissections multiple times with greater efficiency. These digital models also ensure the privacy of human donors, keeping their personal information confidential.
- The limitations and costs of physical lab facilities and equipment
A traditional lab facility requires space, specialized equipment, and ongoing maintenance. Typically, these labs face challenges, i.e., time frames, capacity, and adequate equipment.
However, the emergence of digital cadavers and virtual labs has made it easier for researchers and students to access anatomy by minimizing costs. It allows learners to engage with anatomical studies virtually from any location. Moreover, it reduces the risks associated with physical labs.
- Easy accessibility
Digital tools not only benefit learners but also make teaching more efficient for educators. Anatomical structures can be showcased within seconds to a broad audience. Students can access learning materials anytime and anywhere, acknowledging their busy schedules, including nighttime learning. Digital materials, unlike physical labs, are not bound by operating hours, offering flexibility to both educators and learners.
How Digital Materials and Tools Benefiting in Learning Anatomy?

Digital materials offer many benefits and opportunities for anatomy educators and learners, such as:
- Flexibility and convenience of time and location
Digital materials empower students by enabling them to access anatomy content from anywhere with just a few clicks. Such flexibility gives students personalized experiences and more control over their learning pace.
It also eliminates the barriers of distance and availability. By removing these limitations of distance and availability, digital materials and tools enhance the anatomy studies of students from different countries.
For example, a 3D anatomy model from Anatomy.app allows a student from Indonesia to explore the details of the subject without the need to travel to the US or depend on the scheduling of physical lab sessions. Similarly, a student from India can access the same quality education without the constraints of travel or physical presence in a conventional lab setting. Such apps bridge the geographical gap and provide a convenient and immersive learning experience.
- Enhanced interactivity and engagement with multimedia and gamified elements
Digital materials and tools focus on providing a more immersive and interactive learning experience in the most realistic way possible. Unlike traditional textbooks and lectures, these digital modes rely on 3D models, animations, videos, and audio to demonstrate the anatomical structures. They also use gamified elements like challenges, quizzes, and rewards to motivate and engage the activity of students. This is also what makes learning fun and interesting.
For instance, a student can dissect a digital cadaver using a virtual scalpel and receive instant feedback and scores based on accuracy and performance.
In 2019, a study was conducted on first-year medical students to investigate the feasibility of integrating virtual dissection. The results revealed that 78.7% of students reported improved learning of cardiac anatomy and its applications. Moreover, some students also reported that it was an effective use of lab time.
- Personalized and adaptive learning paths and feedback
Using digital materials modifies the learning journey by allowing students to customize their study plans according to their preferences and goals. For instance, it gives you the choice to select the type of content, mode of delivery, and even the difficulty level based on your learning style.
It also guides you throughout the learning process and provides you with real-time feedback that helps you identify your strengths and weaknesses.
According to a study conducted on 5th-year medical students at Ajou University School of Medicine, simulated labs reduce anxiety levels, increase confidence, and improve clinical performance.
- Collaboration and communication
Digital materials promote effective collaboration and bridge the gap between anatomy students and educators across various regions and disciplines. These tools allow individuals to share their work, perspectives, and other important insights with each other using online platforms like forums, chats, and video conferences.
Such collaboration opportunities make it easier to learn different perspectives and to incorporate knowledge with other fields and domains.
A study showed that virtual reality and cooperative learning in anatomy are effective educational approaches that enhance performance and improve learning outcomes.
Anatomy Beyond the Classroom - How Do Digital Tools Enable This?

Digital cadavers and virtual labs are useful not only for learning anatomy in the classroom but also for exploring and applying anatomy beyond the traditional setting in the following ways:
- 3D modeling of human anatomy
By using digital tools, students can view detailed and realistic 3D models of the human body, which aids in skill development, and enhance anatomical education. The incorporation of 3D technology makes it easy to grasp the concept of complex structures and functions of the human body. It also assists students in identifying the changes that occur in the human body over time due to various illnesses.
These models allow observing anatomy from different perspectives. For instance, you can even zoom in, zoom out, rotate, and dissect the digital model just the way you like. Moreover, it improves the speed of learning and knowledge retention.
- Clinical simulation and practice
The digital tools enable anatomy learners to simulate and practice various clinical scenarios remotely. They can test their knowledge and improve their clinical skills and decision-making abilities in realistic, challenging situations. Such tools will continuously monitor your performance to provide immediate and constructive feedback.
A study was conducted on first-year medical students to determine the educational value of a virtual dissection curriculum. The results found that students had a positive response rate and indicated that it is a valuable tool for understanding anatomy and radiology. Another study concluded that anatomic-specific virtual reality drastically improves surgeon confidence.
- Integration and visualization of anatomy with other fields
Unlike real cadavers, digital models are crucial in connecting anatomy learners with other related fields and topics. It helps students expand their perspective and identify the importance and practical application of anatomy in different domains of health and medicine.
Digital technologies improve students' satisfaction, performance, and overall outcomes. It provides them with the latest data from diverse sources so that students can integrate their knowledge with data from related fields. This holistic approach improves critical skills and prepares the students for comprehensive and real-world applications in medical practice.
- Creation and sharing of anatomy projects and portfolios
The 3D anatomy models increase the confidence of learners and empower them to become active creators. The students can craft their anatomy projects and show their achievements to keep them motivated.
Furthermore, the collaborative nature of digital cadavers and virtual labs helps the students engage with the anatomy community from different regions and disciplines.
Anatomy.app - a Future-Ready Digital Anatomy Learning Platform
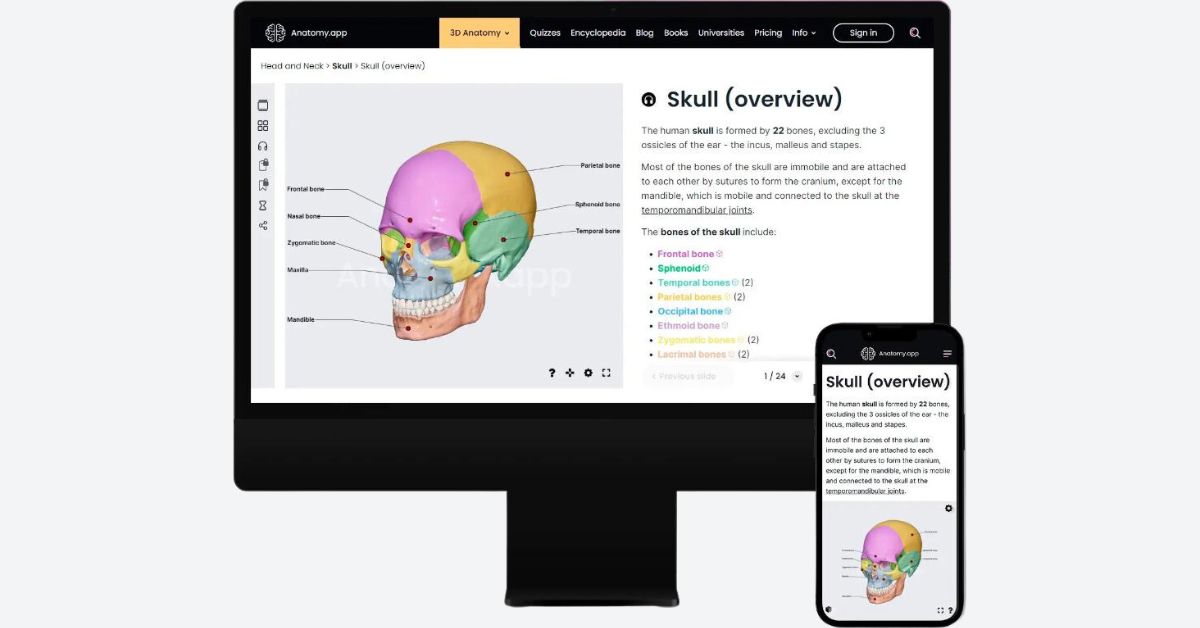
One of the digital tools that will keep up with these future trends and developments is Anatomy.app. This anatomy learning platform offers a wide range of features and benefits, including:
- A 3D anatomy learning platform with immersion and interaction
Anatomy.app is a leading platform for learning anatomy in a 3D environment that is immersive and interactive. The platform uses 3D, 2D, and motion images to make anatomy visual and clear. It also uses color coding, annotations, and a simple yet detailed approach to improve learning. Users can easily explore anatomical structures with these visual aids without getting confused by too much information. This makes anatomy more accessible and enjoyable for medical students, teachers, professionals, and even artists.
- A customized and effective anatomy learning experience
Anatomy.app offers a customized and practical learning experience for anatomy learners. With text and audio support, users can learn about the human body through 3D models and 2D illustrations. The platform lets users learn at their own speed, track their progress, and test their knowledge with quizzes. Users can also organize their studies according to their goals and preferences. The platform's simplicity and detailed and organized materials make learning anatomy easy and efficient.
- An all-in-one and up-to-date anatomy learning tool
Anatomy.app is more than just an anatomy learning app. It is a comprehensive platform that offers various resources on anatomy and medicine. Anatomy.app is the result of a collaborative effort among a diverse team of experts, including medical professionals, 2D and 3D artists, university professors, UI/UX specialists, information designers, and programmers. This multidisciplinary team works in unison to create educational tools of exceptional quality, ensuring that the content is not only up-to-date and accurate but also accessible and engaging. It also showcases a Media Library that displays videos of structures in motion, such as joints. Through their collective expertise, the Anatomy.app offers an unparalleled learning experience, setting a new standard in digital anatomy education.
How Do Digital Anatomy Tools Reach a Wider Audience?

Some of the ways that digital cadavers and virtual labs provide accessibility are:
- Device and platform compatibility
Most digital models can be utilized from any device and platform, such as computers, tablets, smartphones, and web browsers. When students have 24/7 access to learning, without the need for special or expensive equipment or software, learning becomes flexible and promotes an on-the-go learning experience.
- Cost and resource efficiency
Digital tools operate labs in a virtual space, which eliminates the need for physical resources and associated costs. The reduced expenditures and absence of physical infrastructure lead to savings, making education more accessible and affordable. It also aligns with sustainable practices by reducing environmental waste or emissions.
- Learning needs and preferences adaptability
Digital anatomy materials can provide students with high customization. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced learner, the adaptability of these digital tools gives you the freedom to choose different learning methods based on their proficiency levels and much more.
Future Trends and Developments in Digital Anatomy Learning
Digital cadavers and virtual labs are constantly evolving tools that can adapt and innovate to meet anatomy education's changing needs and expectations. Some of the likely future trends and developments in digital anatomy learning are:
- Integrating digital cadavers and virtual labs with other digital technologies and platforms
One of the likely future trends and developments in digital anatomy learning is integrating and collaborating digital cadavers and virtual labs with other digital technologies and platforms, such as augmented reality, virtual reality, artificial intelligence, and cloud computing. These technologies and platforms will enhance the functionality and provide new dimensions for anatomy learning. They will create interactive 3D space simulating real anatomy scenarios, offering a more engaging learning environment.
Furthermore, integrating cloud computing will make it easier to process large and complex anatomy data and models, such as high-resolution and high-fidelity digital cadavers.
- Creating and sharing diverse and customized digital cadavers and virtual labs
Digital cadavers and virtual labs will offer more diverse and customized solutions to anatomy educators based on their preferences. It will enhance the collaborative learning experience by allowing the users to share their customized digital cadavers and virtual labs with other anatomy learners from different regions and disciplines. These advanced features will diversify their perspectives and experiences while enriching their anatomy learning.
- Implying and impacting the broader field of anatomy and medicine
The role of interactive digital technologies in anatomy education will become more prominent in the broader fields of anatomy and medicine, such as research, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of diseases and disorders. These platforms will enable healthcare professionals with clinical skills and encourage them to use their time effectively.
They will also facilitate and support the research and development of new and innovative methods and techniques for studying and understanding the human body, such as 3D printing, bioprinting, or tissue engineering.
Conclusion
Anatomy education is improving greatly with the introduction of digital materials and tools. These resources, such as 3D models, animations, digital cadavers, and virtual labs, provide a more interactive, accessible, and efficient way of learning. This transition from traditional to digital methods overcomes both geographical and logistical obstacles, enhancing the educational experience with unmatched anatomical detail. The future of anatomy education is expected to be more digital, collaborative, and personalized, driven by continuous technological innovations.